| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
13.4
| a) | 2 | 2,60 |
| b) | 13 | 13,625 |
| c) | 17 | 17,75 |
| d) | 23 | 23,875 |
| e) | 36 | 36,8 |
13.5 a) 0,83
13.6
| 4 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 25 | 4 | 39 |
| 4,5 | 5,5 | 3,25 | 8,6 | 25,125 | 4,056 | 39,8 |
14. a) 0,3
Ons kan breuke soos volg na desimale breuke herlei:
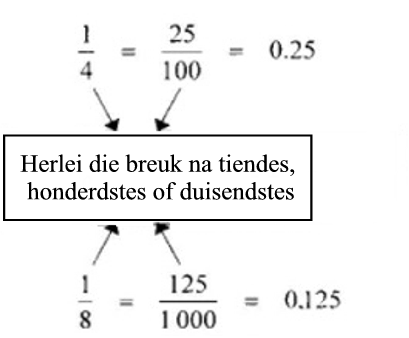
13.2 Het jy geweet?
Ons kan dit ook so bereken:

13.3 Watter van die bogenoemde metodes verkies jy?
Hoekom?

13.5 Gebruik die deelmetode soos by 13.2 en skryf die volgende breuke as desimale breuke:
a) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
b) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
c) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
d) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
13.6 Kan jy die volgende tabel voltooi??
| Onegte breuk | |||||||
| Gemengde getal | |||||||
| Desimale breuk | 3,25 | 4,056 |
14. KOPKRAPPERS!
Probeer eers sonder ’n sakrekenaar! Skryf die volgende breuke as desimale breuke:
a) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
b) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
c) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
15. Onthou jy nog?
Ons noem 0,666666666 . . . ’n repeterende desimaal. Ons skryf dit as .
Net so is 0,454545 . . . ook ’n repeterende desimaal en ons skryf dit .
Ons rond dit gewoonlik af tot 1 of 2 syfers na die desimale teken: word 0,7 of 0,67 en word 0,5 of 0,45
16. Tyd vir self-assessering
|
JA | NEE | |
| Ek kan: | |||
| Desimale breuke met mekaar vergelyk en korrek orden | |||
| Die korrekte verwantskapstekens invul | |||
| Desimale breuke korrek afrond tot: | |||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| Breuke en gemengde getalle korrek na desimale breuke herlei | |||
| Verduidelik wat ’n repeterende desimaal i s |
Leeruitkomste 1: Die leerder is in staat om getalle en die verwantskappe daarvan te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel, en om tydens probleemoplossing bevoeg en met selfvertroue te tel, te skat, te bereken en te kontroleer.
Assesseringstandaard 1.4: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder herken en gebruik ekwivalente vorms van die bogenoemde rasionale getalle, insluitend:
1.4.2 desimale breuke;
Assesseringstandaard 1.0: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder ‘n verskeidenheid strategieë gebruik om oplossings te kontroleer en die redelikheid daarvan te beoordeel.
Leeruitkomste 2: Die leerder is in staat om patrone en verwantskappe te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel en probleme op te los deur algebraïese taal en vaardighede te gebruik.
Assesseringstandaard 2.3: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder voorstellings maak van en verwantskappe tussen veranderlikes gebruik sodat inset- en/of uitsetwaardes op ‘n verskeidenheid maniere bepaal kan word deur die gebruik van:
2.3.1 woordelikse beskrywings;
2.3.3 tabelle.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wiskunde graad 7' conversation and receive update notifications?