| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The output from this program is shown in Figure 4 . As you can see, the concatenated list contains the elements of both of the individual lists.
| Figure 4 . Concatenation program output. |
|---|
Create two lists
Print listA[3.14, 59, 'A string', 1024]
Print listB[2, 4, 6, 16]
Concatenate the listsPrint concatenated list
[3.14, 59, 'A string', 1024, 2, 4, 6, 16] |
The diagram in Figure 5 visualizes the state of the program memory after the three statements in the code box have been executed. This code creates twolist objects and then concatenates them into a third list object pointed to by the variable named listC .
Figure 5. Visualize concatenated lists.
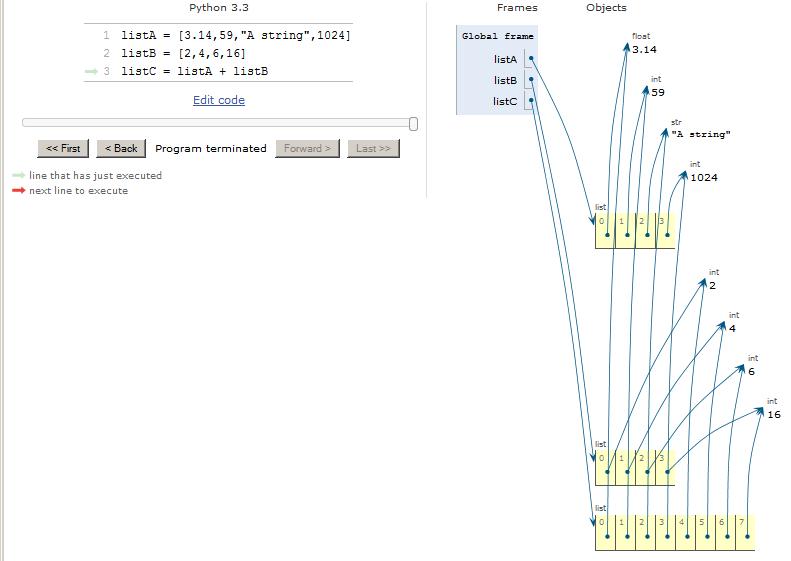
As you can see in Figure 5 , the elements in the new list object point to the objects originally pointed to by the elements in the twooriginal list objects. As you can also see, the order of the elements in the two parts of the new list object preserve theorder of the elements in the two original list objects.
The code in Figure 6 was updated with one additional statement that causes element 0 in one of the original list objects to point to a differentobject of type str containing " OK ".
Figure 6. Change an element in an original list.
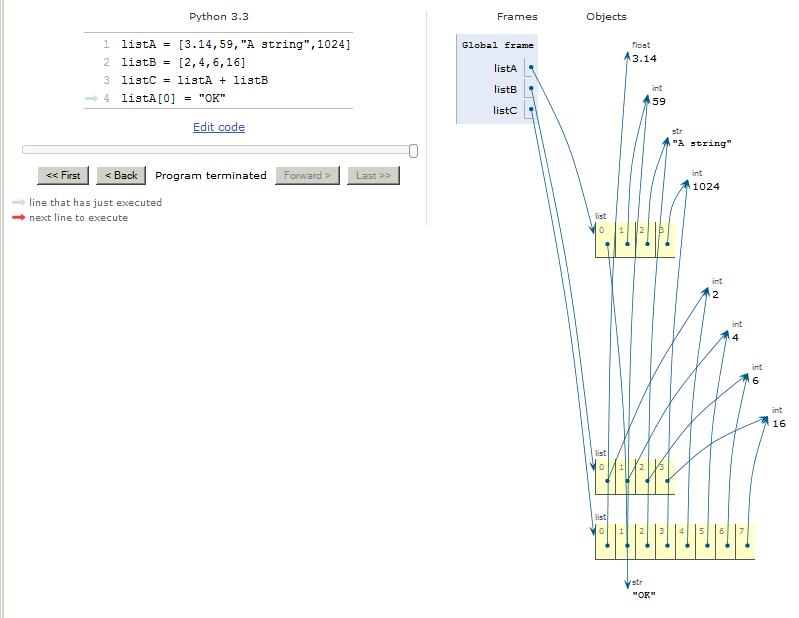
However, element 0 in the concatenated list object pointed to by listC continues to point to the object of type float containing 3.14. The important thing to note here is that the pointer in element 0 in the new list object did not follow suite whenthere was a change in one of the elements in one of the original list objects. It still points to the original float object containing 3.14 and it does not point to the new str object containing "OK" . Therefore, even though the new list object was created by concatenating two original list objects, once created, it is not dependent on thefuture contents of the original list objects. Subsequent changes in the contents of the original list objects are not reflected in the contents of the new list object.
Unlike strings, the values in a list can be modified after the list is created.
The Python program shown in Listing 6 creates and prints a list. Then it uses a subscription to modify and print the list three times.
| Listing 6 . Lists are mutable. |
|---|
# Illustrates mutating lists
##-------------------------------
print("Create and print a list")listA = [3.14,59,"A string",1024]
print(listA)print("Modify the list")
listA[2]= "New string"
print("Print the modified list")print(listA)
print("Modify the list again")listA[3] = listA[3]* 2
print("Print the modified list")print(listA)
print("Modify the list again")listA[2] = 0.99999print("Print the modified list")
print(listA) |
The first modification replaces an existing string in the list with a new string.
The second modification multiplies an integer value in the list by a factor of two.
The third modification replaces a string in the list by a float value of 0.99999.
The output from the program is shown in Figure 7 .
| Figure 7 . List modification program output. |
|---|
Create and print a list
[3.14, 59, 'A string', 1024]Modify the list
Print the modified list[3.14, 59, 'New string', 1024]
Modify the list againPrint the modified list
[3.14, 59, 'New string', 2048]Modify the list again
Print the modified list[3.14, 59, 0.99999, 2048] |
There is a lot more for you to learn about lists that is not included in this module. I will continue this discussion of lists, including moresample programs, in a future module.
This section contains a variety of miscellaneous information.
Financial : Although the Connexions site makes it possible for you to download a PDF file for thismodule at no charge, and also makes it possible for you to purchase a pre-printed version of the PDF file, you should beaware that some of the HTML elements in this module may not translate well into PDF.
I also want you to know that, I receive no financial compensation from the Connexions website even if you purchase the PDF version of the module.
In the past, unknown individuals have copied my modules from cnx.org, converted them to Kindle books, and placed them for sale on Amazon.com showing me as the author. Ineither receive compensation for those sales nor do I know who does receive compensation. If you purchase such a book, please beaware that it is a copy of a module that is freely available on cnx.org and that it was made and published withoutmy prior knowledge.
Affiliation : I am a professor of Computer Information Technology at Austin Community College in Austin, TX.
-end-

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Itse 1359 introduction to scripting languages: python' conversation and receive update notifications?