| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
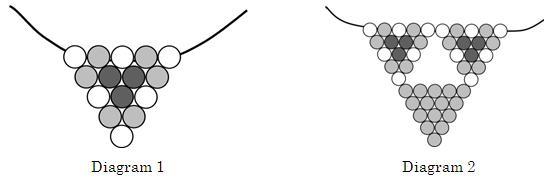
Alice maak hangertjies deur driehoek–motiewe op ‘n draadjie te plaas (soos in diagram 1). Elke motief bestaan uit drie swart krale, ses wit krale en ses gekleurde krale. Dis vir haar belangrik om genoeg krale van elke kleur te koop. Sy wil 50 hangertjies met swart, wit en rooi krale maak; 40 met swart, wit en geel krale; 40 met swart, wit en blou krale en 30 met swart,wit en groen krale.
1. Vraag: Bereken hoeveel krale van elke kleur sy moet koop.
Sy maak ook ‘n groter hangertjie (soos in diagram 2) waar sy drie motiewe kombineer. Die twee boonste motiewe is dieselfde ontwerp as in diagram 1, maar die onderste motief bestaan slegs uit 15 gekleurde krale. Van hierdie hangertjies maak sy net die helfte soveel in elke kleur as die eenvoudige hangertjie.
2. Vraag: Hoeveel krale van elke kleur benodig sy vir hierdie hangertjies?
Die groter hangertjies is bo verwagting gewild, dus besluit sy om groter motiewe te ontwerp en om meer motiewe per hangertjie te gebruik. Die volgende twee diagramme toon haar nuwe planne.

Alice wil vier kleure kombineer in elke motief. Gebruik die diagram om jou eie vier–kleur ontwerp te maak.
3. Vraag: Herhaal die berekening–oefeninge vir hierdie hangertjies.
Hierdie driehoek-motiewe kan natuurlik groter en groter gemaak word. Almal is egter nie geskik vir hangertjies nie!
4. Oefening: Hieronder is gelyksydige driehoek–motiewe 1 tot 4. Teken motiewe 6 en 7 wat verder volg.

Die derde motief hierbo het 1 swart, 3 wit en 6 rooi krale. Jy sal hierna moet verwys in probleem 6 verder aan.
5. Data–insameling: Die krale in die motiewe het elk ‘n deursnit van 1cm. Dus is die sylengte van die eerste motief in die gegewe volgorde 2 cm. Voltooi die tabel hieronder deur na die driehoeke hierbo, asook dié wat jy geteken het, te verwys.
| Sylengte van driehoek in sentimeter | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Aantal krale per driehoek | 3 | 6 | 10 | ||||
| Omtrek van driehoek | 6 | 9 |
6. Ondersoek: Alice maak haar hangertjies deur driehoekmotiewe te kombineer soos in diagram 2 en 4. As sy die 10–kraalmotief gebruik, het die kleinste hanger een motief (grootte 1) en die volgende hanger het drie motiewe (grootte 2) met ‘n driehoek–vormige spasie in die middel. Dink hoe die volgende groottes hangertjies (3, 4, ens.) gaan lyk (of teken hulle) en voltooi onderstaande tabel. Probeer om die laaste kolom ook te voltooi!
| Hangertjie–grootte | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Х |
| Aantal driehoekmotiewe | 6 | 10 | ||||
| Aantal driehoekspasies | ||||||
| Aantal krale per sy van elke driehoekmotief | ||||||
| Totale aantal krale per hangertjie | ||||||
| Aantal swart krale | ||||||
| Totale omtrek van hanger met 1cm krale | 9 |
6. Ondersoek: Doen dieselfde vir die volgende tabel as Alice nou die 15–kraalmotief gebruik (sien die heel eerste diagram).
| Hangertjie–grootte | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Х |
| Aantal driehoekmotiewe | 1 | 3 | ||||
| Aantal driehoekspasies | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Aantal krale per sy van elke driehoekmotief | 5 | 10 | ||||
| Totale aantal krale per hangertjie | 15 | 45 | ||||
| Aantal swart krale | 3 | 9 | ||||
| Totale omtrek van hanger met 1cm krale | 12 | 27 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wiskunde graad 9' conversation and receive update notifications?