| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Up to this point, the product of two binomials has been a trinomial. This is not always the case.
Multiply:
| Distribute. |
|
| Distribute again. | |
| Simplify. | There are no like terms to combine. |
Remember that when you multiply a binomial by a binomial you get four terms. Sometimes you can combine like terms to get a trinomial, but sometimes there are no like terms to combine. Let's look at the last example again and pay particular attention to how we got the four terms.
Where did the first term, come from?
It is the product of the first terms in
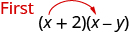
The next term, is the product of the two outer terms.
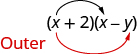
The third term, is the product of the two inner terms.
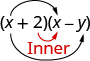
And the last term, came from multiplying the two last terms.
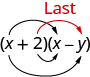
We abbreviate “First, Outer, Inner, Last” as FOIL. The letters stand for ‘First, Outer, Inner, Last’. The word FOIL is easy to remember and ensures we find all four products. We might say we use the FOIL method to multiply two binomials.
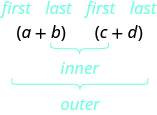
Let's look at again. Now we will work through an example where we use the FOIL pattern to multiply two binomials.
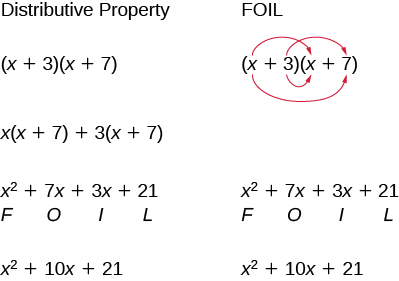
Multiply using the FOIL method:
| Step 1 : Multiply the First terms. |
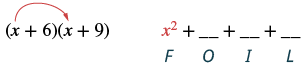 |
| Step 2 : Multiply the Outer terms. |
|
| Step 3 : Multiply the Inner terms. |
|
| Step 4 : Multiply the Last terms. |
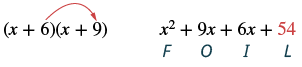 |
| Step 5 : Combine like terms, when possible. |
|
We summarize the steps of the FOIL method below. The FOIL method only applies to multiplying binomials, not other polynomials!
Multiply:
| Step 1 : Multiply the First terms. |
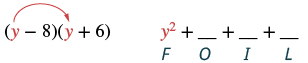 |
| Step 2 : Multiply the Outer terms. |
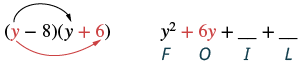 |
| Step 3 : Multiply the Inner terms. |
 |
| Step 4 : Multiply the Last terms. |
 |
| Step 5 : Combine like terms |
|
Multiply:
|
| |
 | |
| Multiply the First terms. |
|
| Multiply the Outer terms. |
|
| Multiply the Inner terms. |
|
| Multiply the Last terms. |
|
| Combine like terms. |
|
Multiply:
|
| |
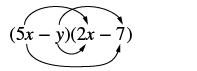 | |
| Multiply the First terms. |
|
| Multiply the Outer terms. |
|
| Multiply the Inner terms. |
|
| Multiply the Last terms. |
|
| Combine like terms. There are none. |
|
The FOIL method is usually the quickest method for multiplying two binomials, but it works only for binomials. You can use the Distributive Property to find the product of any two polynomials. Another method that works for all polynomials is the Vertical Method . It is very much like the method you use to multiply whole numbers. Look carefully at this example of multiplying two-digit numbers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?