| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A large area is usually shown in a small picture on a map. Numbers, letters and pictures are then used to indicate rivers, roads, railway lines, buildings, etc. They are called map symbols. To explain the symbols on a map, a symbol key is used.
Tom has drawn a map (plan) of his classroom:
Tom’s classroom
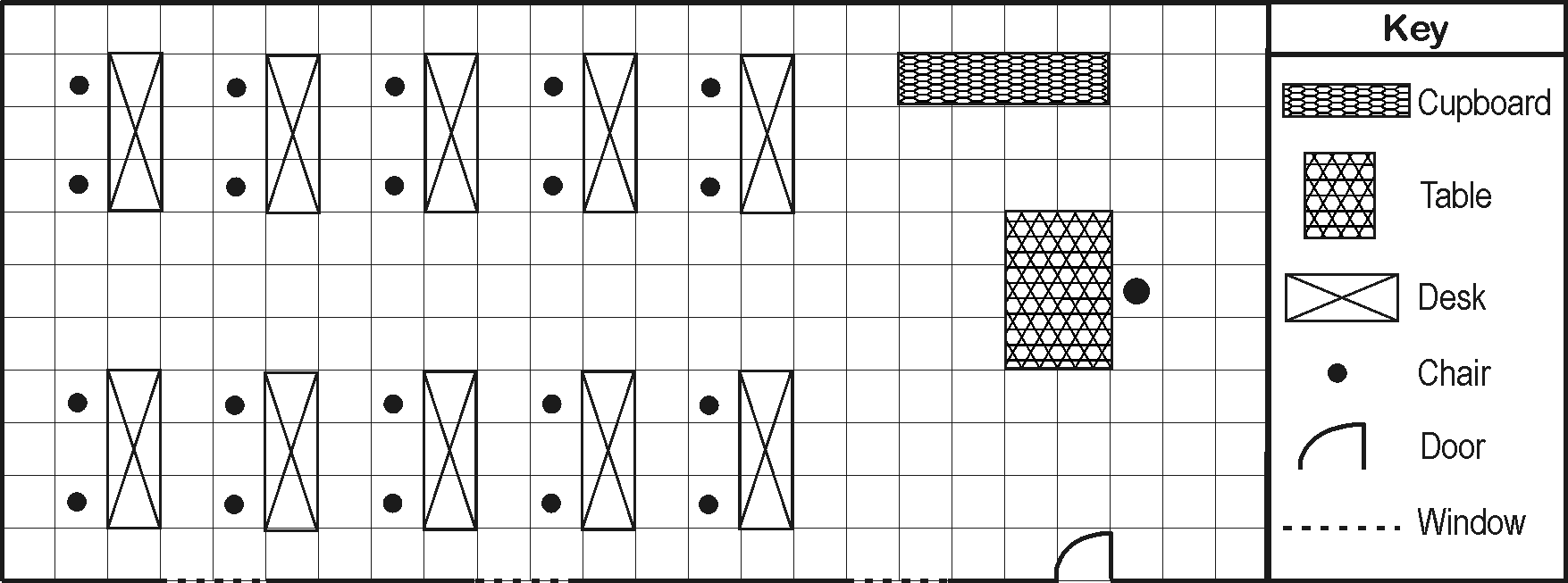
Scale: 1 square = 1 step
The classroom was too big to be drawn on a sheet of paper, and TOM had to REDUCE the classroom. For each step that he took, he used one square on the paper. The tables and other items were also reduced in the same way.
Use the symbol key given and draw a plan of your classroom as you think it will look from the air. You can add to the key if you want to. You can use colour, but work in pencil first to plan it. Use one step for each square. Work on your own.
My classroom
That looks very nice!
Your educator will now give you a plan of your classroom that he/she has drawn up.
1. Compare your educator’s plan with the one that you drew for your classroom. Check to see where you made mistakes.
2. Measure the length of the classroom in steps. It is steps long.
3. Measure the width of the classroom in steps. It is steps wide.
Take a piece of paper and a pencil with you to make notes and sketches of everything you see. Look carefully at the following:
1. The location and shape of the school building.
2. The location and shape of other buildings on the school grounds.
3. The location and shape of the sports fields.
4. The location and shape of the playing fields.
5. The location and shape of the flower gardens.
6. The location of the main entrance gate.
7. The names of the streets on all sides of the school grounds.
8. Make sure where the four main directions are located.
Your educator will now hand out a completed plan of the school grounds:
1. Turn your desks so that you all face NORTH.
2. Study the plan of the school grounds carefully and decide where the four main directions are. Indicate these on the plan.
3. Study the plan of the school grounds carefully and compare it with your notes. Do you agree with the location of the buildings and other objects?
4. Use the key to your plan and colour in the plan accordingly: Example: school buildings – red sports fields - green
5. If you have a problem, your educator can take you outside again to make sure of your facts.
6. Indicate the route from your classroom to the principal’s office with a red arrow.
7. In what direction does the front door of your school face?
8. Write down the names of the various streets around the school in the correct places on the plan.
3. Our immediate surroundings

1. Why do we need a street plan of a city?
……………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………….
2. In what direction does building A lie from building C?
……………………………………………………………………………………….
3. Use red to indicate the shortest route from point C to point D on the map (take one-way streets into consideration).
4. You are standing on the corner of Loop and Leeuwen Streets. Explain to a tourist how to get from that position to point D.
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
Your educator will later give you a map just like this one of your own environment. However, today we are first going to do FIELDWORK again in our own environment.
Your educator will now give each of you a map of your immediate environment. Answer the following questions (note the key to the map):
1. Find your school on the street plan and colour it in.
2. Find your own home, or that of someone you know well, on the map. Colour it in with a different colour.
3. Indicate the route that you followed on your fieldwork outing on the map.
4. Which street is south of your school? ……………………………….
5. Indicate on your own map the important buildings and other features that your educator pointed out during the outing.
The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and
environmental concepts and processes.
We know this when the learner:
1.3 identifies symbols used in different kinds of maps (including plan view, grids and map keys) [works with sources].
1.4 locates places using a simple grid referencing system and directions [works with sources];
1.5 identifies important political boundaries and key human and physical features on large-scale maps [works with sources].
To find places
To find the shortest routes
4. 2 blocks east (in Leeuwen)
2 blocks south

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?