| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Systems manipulate signals, creating output signals derived from their inputs. Why the following are categorized as "simple" willonly become evident towards the end of the course.
Sources produce signals without having input. We like to think of these as having controllable parameters, like amplitude andfrequency. Examples would be oscillators that produce periodic signals like sinusoids and square waves and noise generatorsthat yield signals with erratic waveforms (more about noise subsequently). Simply writing an expression for the signalsthey produce specifies sources. A sine wave generator might be specified by , which says that the source was turned on at to produce a sinusoid of amplitude and frequency .
An amplifier multiplies its input by a constant known as the amplifier gain .
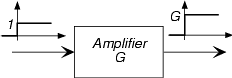
The gain can be positive or negative (if negative, we would say that the amplifier inverts its input) and its magnitude can be greater than one or less than one. If less than one, the amplifieractually attenuates . A real-world example of an amplifier is your home stereo. You control the gain by turningthe volume control.
A system serves as a time delay when the output signal equals the input signal at an earlier time.

Here, is the delay. The way to understand this system is to focus on the time origin: The output at time equals the input at time . Thus, if the delay is positive, the output emerges later thanthe input, and plotting the output amounts to shifting the input plot to the right. The delay can be negative, in whichcase we say the system advances its input. Such systems are difficult to build (they would have toproduce signal values derived from what the input will be ), but we will have occasion to advance signals in time.
Here, the output signal equals the input signal flipped aboutthe time origin.

Again, such systems are difficult to build, but the notion of time reversal occurs frequently in communications systems.
Mentioned earlier was the issue of whether the ordering of systems mattered. In other words, if we have two systems in cascade, does theoutput depend on which comes first? Determine if the ordering matters for the cascade of an amplifier and a delay and for the cascade of atime-reversal system and a delay.
In the first case, order does not matter; in the second it does. "Delay" means . "Time-reverse" means
Case 1 , and the way we apply the gain and delay the signalgives the same result.
Case 2 Time-reverse then delay: . Delay then time-reverse: .
Systems that perform calculus-like operations on their inputs can produce waveforms significantly different than present inthe input. Derivative systems operate in a straightforward way: A first-derivative system would have the input-outputrelationship . Integral systems have the complication that the integral'slimits must be defined. It is a signal theory convention that the elementary integral operation have a lower limit of , and that the value of all signals at equals zero. A simple integrator would have input-output relation
Linear systems are a class of systems rather than having a specific input-output relation. Linearsystems form the foundation of system theory, and are the most important class of systems in communications. They have theproperty that when the input is expressed as a weighted sum of component signals, the output equals the same weighted sum ofthe outputs produced by each component. When is linear,
This general input-output relation property can be manipulated to indicate specific properties shared by all linear systems.
We can find the output of any linear system to a complicated input by decomposing the input into simple signals. The equation above says that when a system is linear, its output to a decomposedinput is the sum of outputs to each input. For example, if the output of any linear system equals
Systems that don't change their input-output relation with time are said to be time-invariant. The mathematical way ofstating this property is to use the signal delay concept described in Simple Systems .
The collection of linear, time-invariant systems are the most thoroughly understood systems. Much of the signal processing and system theorydiscussed here concentrates on such systems. For example, electric circuits are, for the most part, linear andtime-invariant. Nonlinear ones abound, but characterizing them so that you can predict their behavior for any input remainsan unsolved problem.
| Input-Output Relation | Linear | Time-Invariant |
|---|---|---|
| yes | yes | |
| yes | yes | |
| no | yes | |
| yes | yes | |
| yes | yes | |
| yes | yes | |
| yes | no | |
| yes | no | |
| no | yes | |
| no | yes | |
| no | yes |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?