| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Draw the 3D axes
The red, green, and blue 3D axes shown in Figure 1 were produced by the call to the setCoordinateFrame method early in Listing 7 . The setCoordinateFrame method is shown in Listing 11 .
| Listing 11 . The setCoordinateFrame method. |
|---|
private void setCoordinateFrame(Graphics2D g2D){
//Translate the origin to the center.GM01.translate(g2D,0.5*osiWidth,-0.5*osiHeight);
//Draw x-axis in REDg2D.setColor(Color.RED);
GM01.Point3D pointA =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(-75,0,0));
GM01.Point3D pointB =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(75,0,0));
pointA.draw(g2D);pointB.draw(g2D);
new GM01.Line3D(pointA,pointB).draw(g2D);//Draw y-axis in GREENg2D.setColor(Color.GREEN);
pointA =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(0,-75,0));
pointB =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(0,75,0));
pointA.draw(g2D);pointB.draw(g2D);
new GM01.Line3D(pointA,pointB).draw(g2D);//Draw z-axis in BLUEg2D.setColor(Color.BLUE);
pointA =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(0,0,-75));
pointB =new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(0,0,75));
pointA.draw(g2D);pointB.draw(g2D);
new GM01.Line3D(pointA,pointB).draw(g2D);}//end setCoordinateFrame method |
This method is used to set the origin of the off-screen image. It also projects orthogonal 3D axes onto the 2D off-screen image and draws theprojected axes on that image. The axes intersect at the origin in 3D space.
The lengths of the axes are set so as to match the interior dimensions of the box shown in Figure 1 and points are drawn where the axes intersect the surfaces of the box. That was done to enhance the optical illusion of a 3D object on a 2Dplane.
There is nothing in Listing 11 that you haven's seen before, so further explanation should not be required.
End of discussion
That concludes the discussion of the program named GM01test01 . You can view the code that was not discussed here in Listing 28 near the end of the module.
In an earlier module, you learned how to add two or more vectors in 2D. This program will show you how to use the updated game-math library to addvectors in 3D. You also learned about the 2D parallelogram rule and the 2D head-to-tail rule in the earlier module. This program will illustrate thatthose rules also apply to the addition of 3D vectors.
Figure 4 shows the graphic output produced by this program.
Figure 4 Graphic output from the program named GM01test05.
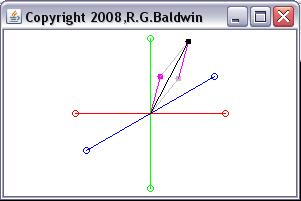
This output shows the addition of a magenta vector to a light gray vector to produce a black vector as the sum of the other two vectors. As you cansee, both the parallelogram rule and the head-to-tail rule are illustrated by the graphic output in Figure 4 .
Very familiar code
Most of the code in this program will be very familiar to you by now. The new code is mostly contained in the method named drawOffScreen , which is shown in Listing 12 . A complete listing of this program is provided in Listing 29 near the end of the module.
| Listing 12 . The drawOffScreen method of the program named GM01test05. |
|---|
//The purpose of this method is to illustrate vector
// addition in 3Dvoid drawOffScreen(Graphics2D g2D){//Translate the origin on the off-screen image, draw a
// pair of orthogonal axes on it that intersect at the// origin, and paint the background white.
setCoordinateFrame(g2D);//Define two vectors that will be added.GM01.Vector3D vecA = new GM01.Vector3D(
new GM01.ColMatrix3D(75,75,75));GM01.Vector3D vecB = new GM01.Vector3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(-15,10,-50));//Create a ref point at the origin for convenience.
GM01.Point3D zeroPoint = new GM01.Point3D(new GM01.ColMatrix3D(0,0,0));//Draw vecA in MAGENTA with its tail at the origin.
g2D.setColor(Color.MAGENTA);vecA.draw(g2D,zeroPoint);//Draw vecB in LIGHT_GRAY with its tail at the head
// of vecA.g2D.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
GM01.Point3D temp =new GM01.Point3D(vecA.getColMatrix());
vecB.draw(g2D,temp);//Draw vecB in LIGHT_GRAY with its tail at the origin.vecB.draw(g2D,zeroPoint);//Draw vecA in MAGENTA with its tail at the head
// of vecB. This completes a trapezoid.g2D.setColor(Color.MAGENTA);
vecA.draw(g2D,new GM01.Point3D(vecB.getColMatrix()));//Add the two vectors.GM01.Vector3D sum = vecA.add(vecB);
//Draw sum in BLACK with its tail at the origin.g2D.setColor(Color.BLACK);
sum.draw(g2D,zeroPoint);}//end drawOffScreen |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Game 2302 - mathematical applications for game development' conversation and receive update notifications?