| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Thanh trùng bằng nhiệt độ cao của nước nóng và hơi nước nóng là phương pháp thanh trùng phổ biến nhất trong sản xuất đồ hộp.
Khi nâng nhiệt độ của môi trường quá nhiệt độ tối thích của vi sinh vật thì hoạt động của vi sinh vật bị chậm lại. Ở nhiệt độ cao, protid của chất nguyên sinh của vi sinh vật bị đông tụ làm cho vi sinh vật bị chết. Quá trình đông tụ protid này không thuận nghịch, nên hoạt động của vi sinh vật không phục hồi sau khi hạ nhiệt.
Từ thực nghiệm đã chỉ sự tiêu diệt vi sinh vật được thể hiện bởi phương trình:
(1)-
Trong đó :
N : lượng vi sinh vật trong sản phẩm sau thời gian t (cfu/ml).
kT: hệ số vận tốc tiêu diệt vi sinh vật ở nhiệt T, tùy theo loại vi sinh vật và tính chất của đồ hộp mà trị số k thay đổi.
t : Thời gian xử lý (phút)
n : Bậc phản ứng
Trong hầu hết trường hợp, bậc phản ứng bằng 1, tiến trình vô hoạt bậc nhất có thể viết như sau:
(2)-
Hay
(3)
Với phương trình vi phân (3) có thể được lấy tích phân theo các điều kiện
ở thời điểm ban đầu t = 0 thì N = No
ở thời điểm t = t thì N = N
(4)
Khi thực hiện tiêu diệt vi sinh vật ở nhiệt độ không đổi, kT = hằng số (quá trình đẳng nhiệt)
Phương trình (4) có thể viết như sau:
(5)
ln (N) – ln (No) = - kT. t(6)
ln
(7)
Hoặc
(8)Từ đó ta có được :
N = No e -kt
Trong đóN : lượng vi sinh vật trong sản phẩm ở thời điểm t (cfu/ml)
No: lượng vi sinh vật ban đầu (cfu/ml)
kT : hệ số vận tốc tiêu diệt vi sinh vật ở nhiệt độ T
t : Thời gian gia nhiệt (phút)
Ở nhiệt độ tiêu diệt vi sinh vật không đổi, lượng vi sinh vật giảm theo hàm số mũ theo thời gian. Điều này có nghĩa tổng số vi sinh vật không thể giảm đến 0. Vì vậy, không thể đảm bảo tuyệt đối rằng tất cả vi sinh vật sẽ bị tiêu diệt bởi một quá trình nào đó.
Nếu vẽ đường biểu diễn về mức độ tiêu diệt vi sinh vật theo thời gian bởi phương trình (8) ta có đồ thị theo hình 4.1

Cũng có thể viết :
(9)
Nếu biểu diễn theo hàm logarite thập phân phương trình (9) đồ thị là một
-
đường thẳng, có hệ số góc biểu thị qua hình 4.2
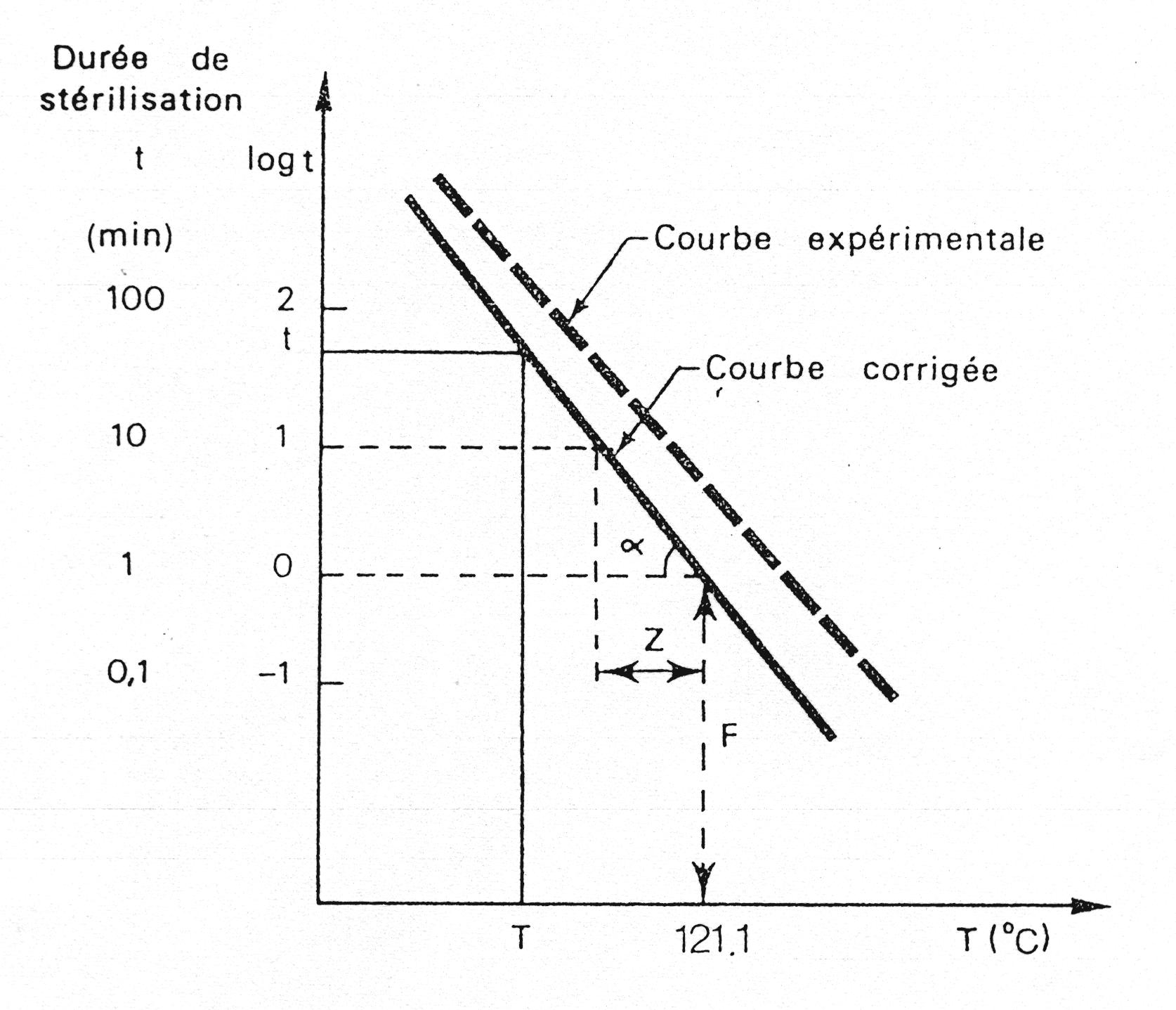
Đường lý thuyếtĐường thực nghiệm

Hình 4.2. Thời gian tiêu diệt vi sinh vật theo mối quan hệ logarite
Với giá trị D là thời gian cần thiết tại một nhiệt độ xác định để tiêu diệt 90% lượng vi sinh vật ban đầu. Được gọi là “thời gian tiêu diệt thập phân”.
Theo hình 4.2 và phương trình (9), ta xây dựng được mối quan hệ giữa hệ số vận tốc k và thời gian D :
-
Phương trình (9) có thể viết :
(10)
Vậy thời gian tiêu diệt vi sinh vật
(11)
Để xác định mức độ tiêu diệt vi sinh vật, cần phải biết trị số D và z biểu thị cho loài vi sinh vật cần tiêu diệt.
(Đường hiệu chỉnh)(Đường thực nghiệm)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Giáo trình công nghệ chế biến thực phẩm đóng hộp' conversation and receive update notifications?