| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How do you spot a phrase in a melody? Just as you often pause between the different sections in a sentence (for example, when you say, "wherever you go, there you are"), the melody usually pauses slightly at the end of each phrase. In vocal music, the musical phrases tend to follow the phrases and sentences of the text. For example, listen to the phrases in the melody of "The Riddle Song" and see how they line up with the four sentences in the song.
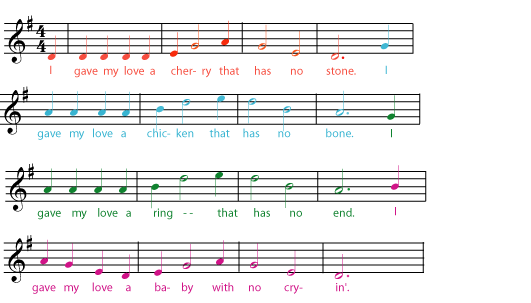
But even without text, the phrases in a melody can be very clear. Even without words, the notes are still grouped into melodic "ideas". Listen to the first strain of Scott Joplin's "The Easy Winners" to see if you can hear four phrases in the melody.
One way that a composer keeps a piece of music interesting is by varying how strongly the end of each phrase sounds like "the end". Usually, full-stop ends come only at the end of the main sections of the music. (See form and cadence for more on this.) By varying aspects of the melody, the rhythm , and the harmony , the composer gives the ends of the other phrases stronger or weaker "ending" feelings. Often, phrases come in definite pairs, with the first phrase feeling very unfinished until it is completed by the second phrase, as if the second phrase were answering a question asked by the first phrase. When phrases come in pairs like this, the first phrase is called the antecedent phrase, and the second is called the consequent phrase. Listen to antecedent and consequent phrases in the tune "Auld Lang Syne".

Of course, melodies don't always divide into clear, separated phrases. Often the phrases in a melody will run into each other, cut each other short, or overlap. This is one of the things that keeps a melody interesting.
Another term that usually refers to a piece of melody (although it can also refer to a rhythm or a chord progression ) is "motif". A motif is a short musical idea - shorter than a phrase - that occurs often in a piece of music. A short melodic idea may also be called a motiv , a motive , a cell , or a figure . These small pieces of melody will appear again and again in a piece of music, sometimes exactly the same and sometimes changed. When a motif returns, it can be slower or faster, or in a different key. It may return "upside down" (with the notes going up instead of down, for example), or with the pitches or rhythms altered.

Most figures and motifs are shorter than phrases, but some of the

Counterpoint has more than one melody at the same time. This tends to change the rules for using and developing melodies, so the terms used to talk about contrapuntal melodies are different, too. For example, the melodic idea that is most important in a fugue is called its subject . Like a motif, a subject has often changed when it reappears, sounding higher or lower, for example, or faster or slower. For more on the subject (pun intended), please see Counterpoint .
A longer section of melody that keeps reappearing in the music - for example, in a "theme and variations" - is often called a theme . Themes generally are at least one phrase long and often have several phrases. Many longer works of music, such as symphony movements, have more than one melodic theme.

The musical scores for movies and television can also contain melodic themes , which can be developed as they might be in a symphony or may be used very much like operatic leitmotifs . For example, in the music John Williams composed for the Star Wars movies, there are melodic themes that are associated with the main characters. These themes are often complete melodies with many phrases, but a single phrase can be taken from the melody and used as a motif. A single phrase of Ben Kenobi's Theme , for example, can remind you of all the good things he stands for, even if he is not on the movie screen at the time.
Melody is a particularly easy concept to convey to children, since attention to a piece of music is naturally drawn to the melody. If you would like to introduce some of these concepts and terms to children, please see A Melody Activity , The Shape of a Melody , Melodic Phrases , and Theme and Motif in Music .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The basic elements of music' conversation and receive update notifications?