| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
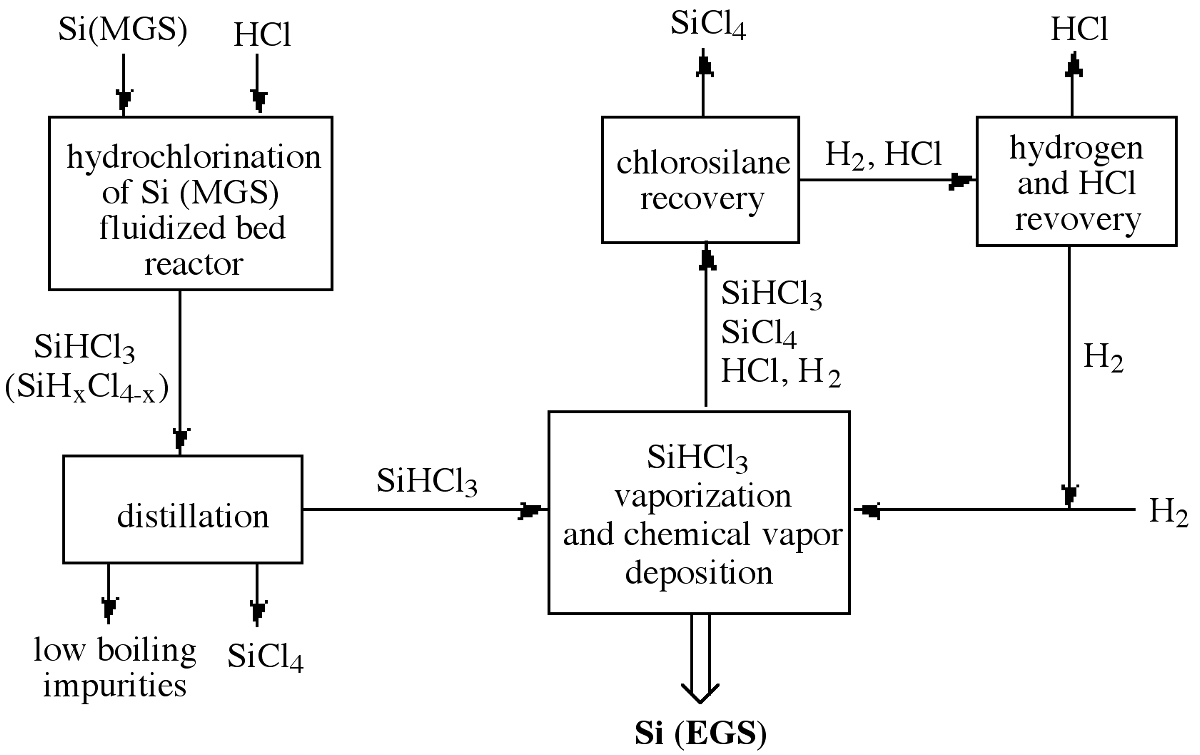
In addition to the formation of silicon, the HCl coproduct reacts with the SiHCl 3 reactant to form silicon tetrachloride (SiCl 4 ) and hydrogen as major byproducts of the process, [link] . This reaction represents a major disadvantage with the Seimens process: poor efficiency of silicon and chlorine consumption. Typically, only 30% of the silicon introduced into CVD reactor is converted into high-purity polysilicon.
In order to improve efficiency the HCl, SiCl 4 , H 2 , and unreacted SiHCl 3 are separated and recovered for recycling. [link] illustrates the entire chlorosilane process starting with MGS and including the recycling of the reaction byproducts to achieve high overall process efficiency. As a consequence, the production cost of high-purity EGS depends on the commercial usefulness of the byproduct, SiCl 4 . Additional disadvantages of the Seimens process are derived from its relatively small batch size, slow growth rate, and high power consumption. These issues have lead to the investigation of alternative cost efficient routes to EGS.
An alternative process for the production of EGS that has begun to receive commercial attention is the pyrolysis of silane (SiH 4 ). The advantages of producing EGS from SiH 4 instead of SiHCl 3 are potentially lower costs associated with lower reaction temperatures, and less harmful byproducts. Silane decomposes<900 °C to give silicon and hydrogen, [link] .
Silane may be prepared by a number of routes, each having advantages with respect to purity and production cost. The simplest process involves the direct reaction of MGS powders with magnesium at 500 °C in a hydrogen atmosphere, to form magnesium silicide (Mg 2 Si). The magnesium silicide is then reacted with ammonium chloride in liquid ammonia below 0 °C, [link] .
This process is ideally suited to the removal of boron impurities (a p-type dopant in Si), because the diborane (B 2 H 6 ) produced during the reaction forms the Lewis acid-base complex, H 3 B(NH 3 ), whose volatility is sufficiently lower than SiH 4 , allowing for the purification of the latter. It is possible to prepare EGS with a boron content of ≤ 20 ppt using SiH 4 synthesized in this manner. However, phosphorus (another dopant) in the form of PH 3 may be present as a contaminant requiring subsequent purification of the SiH 4 .
Alternative routes to SiH 4 involve the chemical reduction of SiCl 4 by either lithium hydride ( [link] ), lithium aluminum hydride ( [link] ), or via hydrogenation in the presence of elemental silicon ( [link] - [link] ). The hydride reduction reactions may be carried-out on relatively large scales (ca. 50 kg), but only batch processes. In contrast, Union Carbide has adapted the hydrogenation to a continuous process, involving disproportionation reactions of chlorosilanes ( [link] - [link] ) and the fractional distillation of silane ( [link] ).
Pyrolysis of silane on resistively heated polysilicon filaments at 700-800 °C yields polycrystalline EGS. As noted above, the EGS formed has remarkably low boron impurities compared with material prepared from trichlorosilane. Moreover, the resulting EGS is less contaminated with transition metals from the reactor container because SiH 4 decomposition does not cause as much of a corrosion problem as is observed with halide precursor compounds.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of electronic materials' conversation and receive update notifications?