| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A comparison of the two types of structural ecosystem models shows strength in both. Food chains are more flexible for analytical modeling, are easier to follow, and are easier to experiment with, whereas food web models more accurately represent ecosystem structure and dynamics, and data can be directly used as input for simulation modeling.
Head to this online interactive simulator to investigate food web function. In the Interactive Labs box, under Food Web , click Step 1 . Read the instructions first, and then click Step 2 for additional instructions. When you are ready to create a simulation, in the upper-right corner of the Interactive Labs box, click OPEN SIMULATOR .
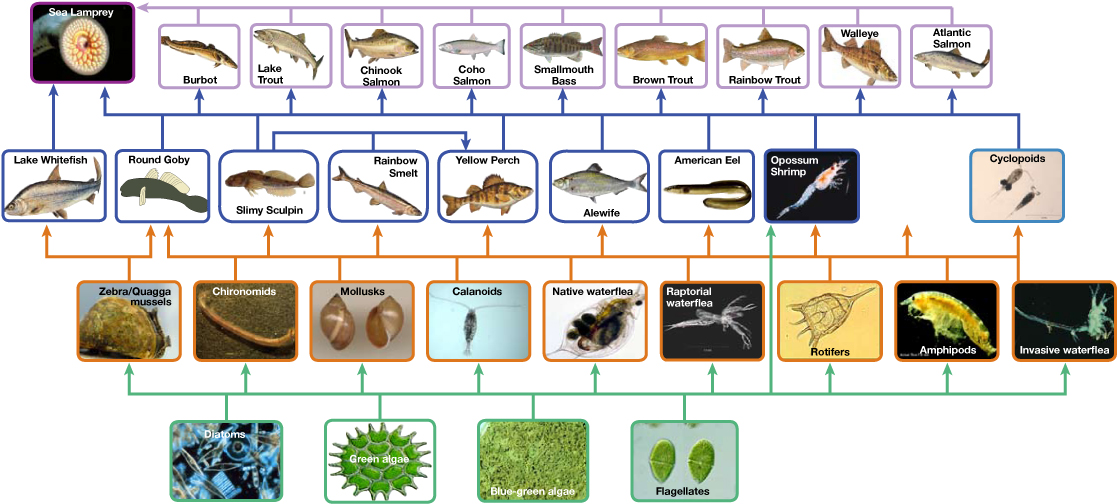
Two general types of food webs are often shown interacting within a single ecosystem. A grazing food web (such as the Lake Ontario food web in [link] ) has plants or other photosynthetic organisms at its base, followed by herbivores and various carnivores. A detrital food web consists of a base of organisms that feed on decaying organic matter (dead organisms), called decomposers or detritivores. These organisms are usually bacteria or fungi that recycle organic material back into the biotic part of the ecosystem as they themselves are consumed by other organisms. As all ecosystems require a method to recycle material from dead organisms, most grazing food webs have an associated detrital food web. For example, in a meadow ecosystem, plants may support a grazing food web of different organisms, primary and other levels of consumers, while at the same time supporting a detrital food web of bacteria, fungi, and detrivorous invertebrates feeding off dead plants and animals.
The three-spines stickleback ( Gasterosteus aculeatus ) is a freshwater fish that evolved from a saltwater fish to live in freshwater lakes about 10,000 years ago, which is considered a recent development in evolutionary time ( [link] ). Over the last 10,000 years, these freshwater fish then became isolated from each other in different lakes. Depending on which lake population was studied, findings showed that these sticklebacks then either remained as one species or evolved into two species. The divergence of species was made possible by their use of different areas of the pond for feeding called micro niches.
Dr. Harmon and his team created artificial pond microcosms in 250-gallon tanks and added muck from freshwater ponds as a source of zooplankton and other invertebrates to sustain the fish. In different experimental tanks they introduced one species of stickleback from either a single-species or double-species lake.
Over time, the team observed that some of the tanks bloomed with algae while others did not. This puzzled the scientists, and they decided to measure the water's dissolved organic carbon (DOC), which consists of mostly large molecules of decaying organic matter that give pond-water its slightly brownish color. It turned out that the water from the tanks with two-species fish contained larger particles of DOC (and hence darker water) than water with single-species fish. This increase in DOC blocked the sunlight and prevented algal blooming. Conversely, the water from the single-species tank contained smaller DOC particles, allowing more sunlight penetration to fuel the algal blooms.
This change in the environment, which is due to the different feeding habits of the stickleback species in each lake type, probably has a great impact on the survival of other species in these ecosystems, especially other photosynthetic organisms. Thus, the study shows that, at least in these ecosystems, the environment and the evolution of populations have reciprocal effects that may now be factored into simulation models.

Visit The Darwin Project to view a variety of ecosystem models.
Ecosystems exist on land, at sea, in the air, and underground. Different ways of modeling ecosystems are necessary to understand how environmental disturbances will affect ecosystem structure and dynamics. Conceptual models are useful to show the general relationships between organisms and the flow of materials or energy between them. Analytical models are used to describe linear food chains, and simulation models work best with holistic food webs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?