| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
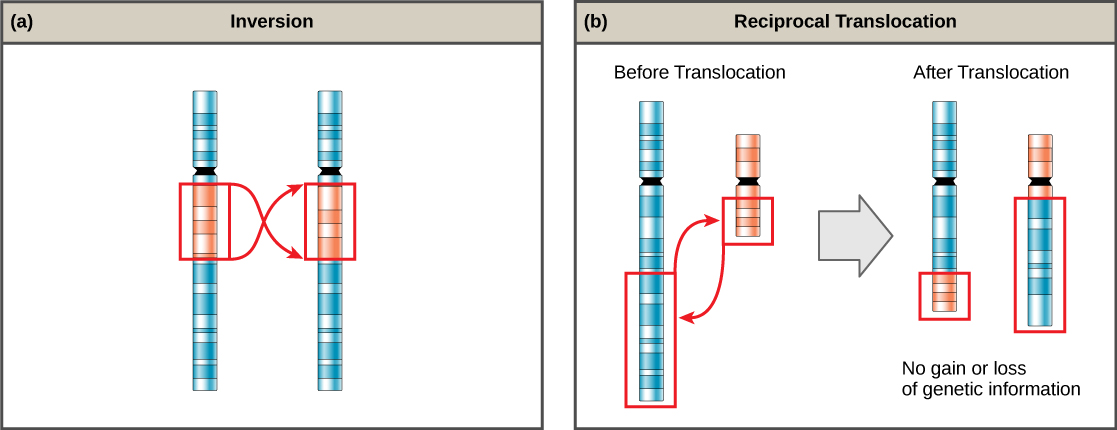
A chromosome inversion is the detachment, 180° rotation, and reinsertion of part of a chromosome ( [link] ). Unless they disrupt a gene sequence, inversions only change the orientation of genes and are likely to have more mild effects than aneuploid errors.
The chromosome 18 inversion is believed to have occurred in early humans following their divergence from a common ancestor with chimpanzees approximately five million years ago. Researchers have suggested that a long stretch of DNA was duplicated on chromosome 18 of an ancestor to humans, but that during the duplication it was inverted (inserted into the chromosome in reverse orientation.
A comparison of human and chimpanzee genes in the region of this inversion indicates that two genes— ROCK1 and USP14 —are farther apart on human chromosome 18 than they are on the corresponding chimpanzee chromosome. This suggests that one of the inversion breakpoints occurred between these two genes. Interestingly, humans and chimpanzees express USP14 at distinct levels in specific cell types, including cortical cells and fibroblasts. Perhaps the chromosome 18 inversion in an ancestral human repositioned specific genes and reset their expression levels in a useful way. Because both ROCK1 and USP14 code for enzymes, a change in their expression could alter cellular function. It is not known how this inversion contributed to hominid evolution, but it appears to be a significant factor in the divergence of humans from other primates. V Goidts, et al., “Segmental duplication associated with the human-specific inversion of chromosome 18: a further example of the impact of segmental duplications on karyotype and genome evolution in primates,” Human Genetics , 115 (2004):116–22.
A translocation occurs when a segment of a chromosome dissociates and reattaches to a different, nonhomologous chromosome. Translocations can be benign or have devastating effects, depending on how the positions of genes are altered with respect to regulatory sequences. Notably, specific translocations have been associated with several cancers and with schizophrenia. Reciprocal translocations result from the exchange of chromosome segments between two nonhomologous chromosomes such that there is no gain or loss of genetic information ( [link] ).
The number, size, shape, and banding pattern of chromosomes make them easily identifiable in a karyogram and allow for the assessment of many chromosomal abnormalities. Disorders in chromosome number, or aneuploidies, are typically lethal to the embryo, although a few trisomic genotypes are viable. Because of X inactivation, aberrations in sex chromosomes typically have milder effects on an individual. Aneuploidies also include instances in which segments of a chromosome are duplicated or deleted. Chromosome structures also may be rearranged, for example by inversion or translocation. Both of these aberrations can result in negative effects on development, or death. Because they force chromosomes to assume contorted pairings during meiosis I, inversions and translocations are often associated with reduced fertility because of the likelihood of nondisjunction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?