This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses how to divide whole numbers. By the end of the module students should be able to be able to divide a whole number by a single or multiple digit divisor and interpret a calculator statement that a division results in a remainder.
Section overview
- Division with a Single Digit Divisor
- Division with a Multiple Digit Divisor
- Division with a Remainder
- Calculators
Division with a single digit divisor
Our experience with multiplication of whole numbers allows us to perform such divisions as
. We perform the division by performing the corresponding multiplication,
. Each division we considered in
[link] had a one-digit quotient. Now we will consider divisions in which the quotient may consist of two or more digits. For example,
.
Let's examine the division
. We are asked to determine how many 5's are contained in 75. We'll approach the problem in the following way.
- Make an educated guess based on experience with multiplication.
- Find how close the estimate is by multiplying the estimate by 5.
- If the product obtained in step 2 is less than 75, find out how much less by subtracting it from 75.
- If the product obtained in step 2 is greater than 75, decrease the estimate until the product is less than 75. Decreasing the estimate makes sense because we do not wish to exceed 75.
We can suggest from this discussion that the process of division consists of
The four steps in division
- an educated guess
- a multiplication
- a subtraction
- bringing down the next digit (if necessary)
The educated guess can be made by determining how many times the divisor is contained in the dividend by using only one or two digits of the dividend.
Sample set a
Find
.
Rewrite the problem using a division bracket.
Make an educated guess by noting that one 5 is contained in 75 at most 10 times.
Since 7 is the tens digit, we estimate that 5 goes into 75 at most 10 times.
Now determine how close the estimate is.
10 fives is
. Subtract 50 from 75.
Estimate the number of 5's in 25.
There are exactly 5 fives in 25.
Check:
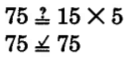
Thus,
.
The notation in this division can be shortened by writing.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Find
.
Rewrite the problem using a division bracket.
8 goes into 49 at most 6 times, and 9 is in the hundreds column. We'll guess 600.
Then,
.
8 goes into 14 at most 1 time, and 4 is in the tens column. We'll guess 10.
8 goes into 64 exactly 8 times.
600 eights + 10 eights + 8 eights = 618 eights.
Check:
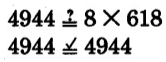
Thus,
.
As in the first problem, the notation in this division can be shortened by eliminating the subtraction signs and the zeros in each educated guess.

Got questions? Get instant answers now!
![]()
![]()

