| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
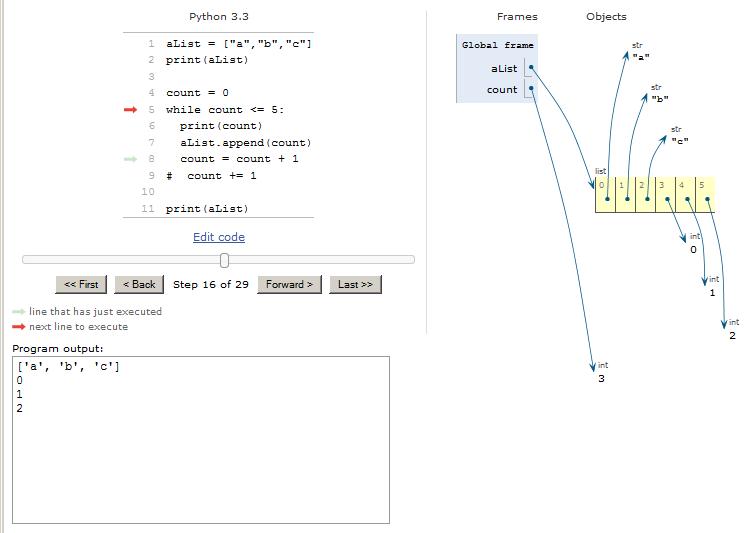
The code in Listing 2 begins by creating a list named aList . The list is initially populated with the strings "a", "b", and "c". Then thatlist is printed producing the first line of output text shown in Figure 2 .
Following that, a variable named count is created and initialized with the value 0. This variable will be used to control the numberof iterations in the while loop.
The next four lines of code in Listing 2 constitute a while loop. The first line in the while loop contains a decision structure terminated by a colon.
Recall that the initial value of count is 0. The behavior of the first line in the while loop can be paraphrased as follows:
While the value of count is less than or equal (note the relational operator that consists of a left angle bracket and an equal character) to the literal value 5, execute all of the statements that follow the colon at the same indentation level.
Stated differently, for as long as the conditional clause (count less than or equal to5) continues to be true, execute all of the statements that follow the colon at the same indentation level. When the conditional clause is nolonger true, skip the indented statements and transfer control to whatever follows the indented statements.
In this case, there are three statements (followed by a comment) at the same indentation level following the colon. The first of the three statements prints the current valuestored in the variable named count as shown by the second line of text in Figure 2 .
You learned in an earlier module that a list is a mutable sequence type. The term mutable means that the values stored in the list can be modified after thelist is created.
There are a dozen or more operations that can be performed on a list to modify its contents. One of those operations is append(x) . This operation appends the value of x to the end of the list. For the time being, I am going to refer to append(x) as a method belonging to the list object.
The second indented statement in Listing 2 calls the append method on the list, appending the value currently stored in the variable named count to the end of the list. This will increase the length of the list by one.
Note that the append method is called on the list by joining the name of the list ( aList ) to the name of the append method using a period as a joining operator. The item that is to be appended to the list (the value of count ) is passed as a parameter to the append method.
The last statement in the indented group of three statements increments or adds one to the value stored in the variable named count . This statement retrieves the value stored in the variable named count , adds one to that value, and stores the sum back in the variable named count replacing the value that was previously stored there.
The comment following that statement shows a shorthand way to accomplish the exact same thing.
Incrementing the counter variable is critical to the proper operation of the script. If the counter variable is not incremented within the body of the loop, it will remain less than 5 forever and the conditional clause at the top of the while loop ( count less than or equal to 5) will be true forever. This will cause the loop to continue looping forever. This is often referred toan infinite loop .
The code in Listing 2 increments the counter variable once during each iteration of the loop. As you can see from the program output in Figure 2 , this causes it to count from 0 through 5 inclusive.
Each time the last indented statement in the body of the loop finishes executing, control goes back to the top of theloop where the value of count is tested against the literal value 5. (You can see this happening by stepping through the visualization.) When the count finally reaches 6,
This causes the last statement in Listing 2 to be executed. This statement prints thecurrent state of the list. As you can see in Figure 2 , the length of the list has been increased from the original length of 3 elements to a new length of 9elements. The list now contains the three original strings plus six new elements, which are the countervalues from 0 through 5 inclusive.
I encourage you to copy the code from Listing 2 . Execute the code and confirm that you get the same results as those shown in Figure 2 . Experiment with the code, making changes, and observing the results of your changes. Make certain that youcan explain why your changes behave as they do.
I also encourage you to create and step through the visualization shown in Figure 3 .
This section contains a variety of miscellaneous information.
Financial : Although the Connexions site makes it possible for you to download a PDF file for thismodule at no charge, and also makes it possible for you to purchase a pre-printed version of the PDF file, you should beaware that some of the HTML elements in this module may not translate well into PDF.
I also want you to know that, I receive no financial compensation from the Connexions website even if you purchase the PDF version of the module.
In the past, unknown individuals have copied my modules from cnx.org, converted them to Kindle books, and placed them for sale on Amazon.com showing me as the author. Ineither receive compensation for those sales nor do I know who does receive compensation. If you purchase such a book, please beaware that it is a copy of a module that is freely available on cnx.org and that it was made and published withoutmy prior knowledge.
Affiliation : I am a professor of Computer Information Technology at Austin Community College in Austin, TX.
-end-

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Itse 1359 introduction to scripting languages: python' conversation and receive update notifications?