| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
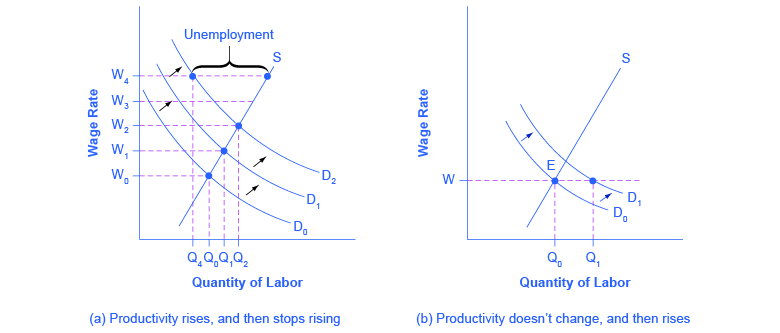
The late 1990s provide an opposite example: instead of the surprise decline in productivity in the 1970s, productivity unexpectedly rose in the mid-1990s. The annual growth rate of real output per hour of labor increased from 1.7% from 1980–1995, to an annual rate of 2.6% from 1995–2001. Let’s simplify the situation a bit, so that the economic lesson of the story is easier to see graphically, and say that productivity had not been increasing at all in earlier years, so the intersection of the labor market was at point E in [link] (b), where the demand curve for labor (D 0 ) intersects the supply curve for labor. As a result, real wages were not increasing. Now, productivity jumps upward, which shifts the demand for labor out to the right, from D 0 to D 1 . At least for a time, however, wages are still being set according to the earlier expectations of no productivity growth, so wages do not rise. The result is that at the prevailing wage level (W), the quantity of labor demanded (Qd) will for a time exceed the quantity of labor supplied (Qs), and unemployment will be very low—actually below the natural level of unemployment for a time. This pattern of unexpectedly high productivity helps to explain why the unemployment rate stayed below 4.5%—quite a low level by historical standards—from 1998 until after the U.S. economy had entered a recession in 2001.
Average levels of unemployment will tend to be somewhat higher on average when productivity is unexpectedly low, and conversely, will tend to be somewhat lower on average when productivity is unexpectedly high. But over time, wages do eventually adjust to reflect productivity levels.
Public policy can also have a powerful effect on the natural rate of unemployment. On the supply side of the labor market, public policies to assist the unemployed can affect how eager people are to find work. For example, if a worker who loses a job is guaranteed a generous package of unemployment insurance, welfare benefits, food stamps, and government medical benefits, then the opportunity cost of being unemployed is lower and that worker will be less eager to seek a new job.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?