| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find the prime factorization of using the factor tree method.
|
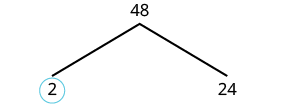
We can start our tree using any factor pair of 48. Let's use 2 and 24. We circle the 2 because it is prime and so that branch is complete. |
 |
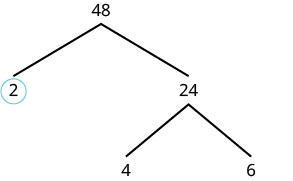
| Now we will factor 24. Let's use 4 and 6. |
 |
|
Neither factor is prime, so we do not circle either.
We circle the 2s and the 3 since they are prime. Now all of the branches end in a prime. |
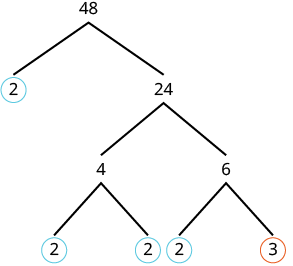 |
| Write the product of the circled numbers. | |
| Write in exponential form. |
Check this on your own by multiplying all the factors together. The result should be
Find the prime factorization using the factor tree method:
2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 5, or 2 4 ⋅ 5
Find the prime factorization using the factor tree method:
2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5, or 2 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5
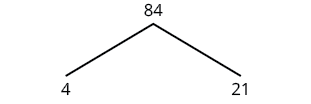
Find the prime factorization of 84 using the factor tree method.
|
We start with the factor pair 4 and 21. Neither factor is prime so we factor them further. |
 |
| Now the factors are all prime, so we circle them. |
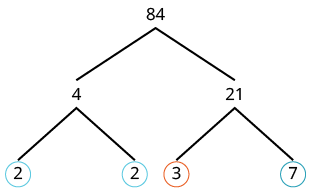 |
| Then we write 84 as the product of all circled primes. |
|
Draw a factor tree of
Find the prime factorization using the factor tree method:
2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 7, or 2 ⋅ 3 2 ⋅ 7
Find the prime factorization using the factor tree method:
2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 7, or 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 7 2
The ladder method is another way to find the prime factors of a composite number. It leads to the same result as the factor tree method. Some people prefer the ladder method to the factor tree method, and vice versa.
To begin building the “ladder,” divide the given number by its smallest prime factor. For example, to start the ladder for we divide by the smallest prime factor of
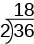
To add a “step” to the ladder, we continue dividing by the same prime until it no longer divides evenly.
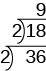
Then we divide by the next prime; so we divide by
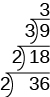
We continue dividing up the ladder in this way until the quotient is prime. Since the quotient, is prime, we stop here.
Do you see why the ladder method is sometimes called stacked division?
The prime factorization is the product of all the primes on the sides and top of the ladder.
Notice that the result is the same as we obtained with the factor tree method.
Find the prime factorization of using the ladder method.
| Divide the number by the smallest prime, which is 2. |
|
| Continue dividing by 2 until it no longer divides evenly. |
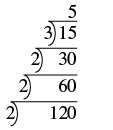 |
| Divide by the next prime, 3. |
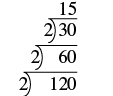 |
| The quotient, 5, is prime, so the ladder is complete. Write the prime factorization of 120. |
|
Check this yourself by multiplying the factors. The result should be

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?