| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section we examine parametric equations and their graphs. In the two-dimensional coordinate system, parametric equations are useful for describing curves that are not necessarily functions. The parameter is an independent variable that both x and y depend on, and as the parameter increases, the values of x and y trace out a path along a plane curve. For example, if the parameter is t (a common choice), then t might represent time. Then x and y are defined as functions of time, and can describe the position in the plane of a given object as it moves along a curved path.
Consider the orbit of Earth around the Sun. Our year lasts approximately 365.25 days, but for this discussion we will use 365 days. On January 1 of each year, the physical location of Earth with respect to the Sun is nearly the same, except for leap years, when the lag introduced by the extra day of orbiting time is built into the calendar. We call January 1 “day 1” of the year. Then, for example, day 31 is January 31, day 59 is February 28, and so on.
The number of the day in a year can be considered a variable that determines Earth’s position in its orbit. As Earth revolves around the Sun, its physical location changes relative to the Sun. After one full year, we are back where we started, and a new year begins. According to Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, the shape of the orbit is elliptical, with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse. We study this idea in more detail in Conic Sections .
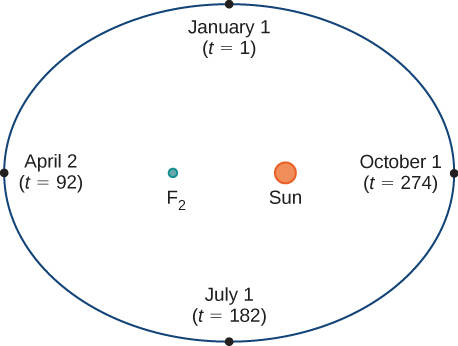
[link] depicts Earth’s orbit around the Sun during one year. The point labeled is one of the foci of the ellipse; the other focus is occupied by the Sun. If we superimpose coordinate axes over this graph, then we can assign ordered pairs to each point on the ellipse ( [link] ). Then each x value on the graph is a value of position as a function of time, and each y value is also a value of position as a function of time. Therefore, each point on the graph corresponds to a value of Earth’s position as a function of time.
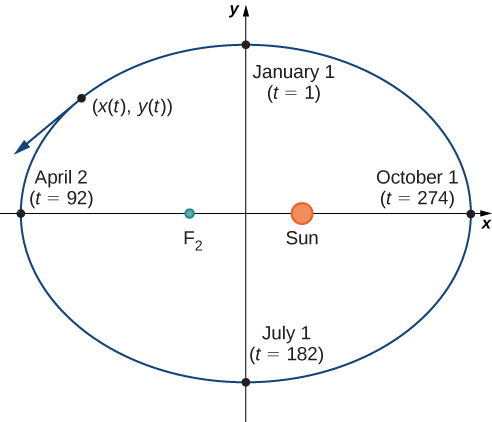
We can determine the functions for and thereby parameterizing the orbit of Earth around the Sun. The variable is called an independent parameter and, in this context, represents time relative to the beginning of each year.
A curve in the plane can be represented parametrically. The equations that are used to define the curve are called parametric equations .
If x and y are continuous functions of t on an interval I , then the equations
are called parametric equations and t is called the parameter . The set of points obtained as t varies over the interval I is called the graph of the parametric equations. The graph of parametric equations is called a parametric curve or plane curve , and is denoted by C .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?