| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As electrons move through the proteins that reside between PSII and PSI, they lose energy. That energy is used to move hydrogen atoms from the stromal side of the membrane to the thylakoid lumen. Those hydrogen atoms, plus the ones produced by splitting water, accumulate in the thylakoid lumen and will be used synthesize ATP in a later step. Because the electrons have lost energy prior to their arrival at PSI, they must be re-energized by PSI, hence, another photon is absorbed by the PSI antenna. That energy is relayed to the PSI reaction center (called P700 ). P700 is oxidized and sends a high-energy electron to NADP + to form NADPH. Thus, PSII captures the energy to make ATP, and PSI captures the energy to reduce NADP + into NADPH. The two photosystems work in concert, in part, to guarantee that the production of NADPH will roughly equal the production of ATP. Other mechanisms exist to fine tune that ratio to exactly match the chloroplast’s constantly changing energy needs.
In chemiosmosis, the free energy from the series of redox reactions just described is used to pump hydrogen ions (protons) across the membrane. The uneven distribution of H + ions across the thylakoid membrane establishes both concentration and electrical gradients (thus, an electrochemical gradient), owing to the hydrogen ions’ positive charge and their aggregation on one side of the membrane.
If the thylakoid membrane were open to diffusion by the hydrogen ions, the ions would tend to diffuse back across into the matrix, driven by their electrochemical gradient. Recall that many ions cannot diffuse through the nonpolar regions of phospholipid membranes without the aid of ion channels. Similarly, hydrogen ions in the thylakoid lumen can only pass through the thylakoid membrane through an integral membrane protein called ATP synthase ( [link] ). This complex protein acts as a tiny generator, turned by the force of the hydrogen ions diffusing through it, down their electrochemical gradient. The turning parts of this molecular machine facilitates the addition of a phosphate to ADP, forming ATP, using the potential energy of the hydrogen ion gradient.
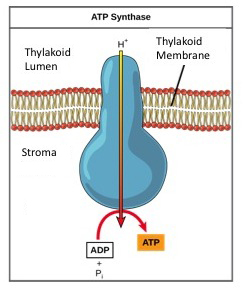
As a review, the buildup of hydrogen ions inside the thylakoid lumen creates a concentration gradient. The passive diffusion of hydrogen ions from high concentration (in the thylakoid lumen) to low concentration (in the stroma) is harnessed to create ATP. The ions build up energy because of diffusion and because they all have the same electrical charge, repelling each other. To release this energy, hydrogen ions will rush through any opening, similar to water jetting through a hole in a dam. In the thylakoid, that opening is a passage through a specialized protein channel called the ATP synthase. The energy released by the hydrogen ion stream allows ATP synthase to attach a third phosphate group to ADP, which forms a molecule of ATP ( [link] ). The flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis because the ions move from an area of high to an area of low concentration through a semi-permeable structure.
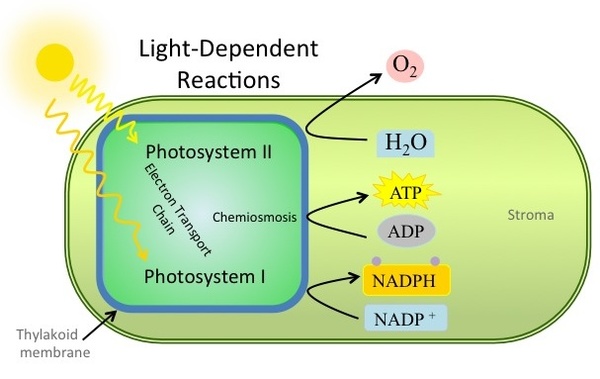
Light energy is harvested and transformed into short term chemical energy during the light-dependent reactions. The pigments in the reaction center of photosytem II absorb light energy and excite electrons into the electron transport chain. To replace the electrons excited in photosystem II, water is spilt releasing electrons, H
+ ions and oxygen gas. As the electrons move through the electron transport chain, energy, release by the movement of electrons, is used to produce a H
+ ion gradient inside the thylakoid. The process of chemiosmosis uses the H
+ concentration to produce ATP. After flowing through the electron transport chain, the electrons enter photosystem I. The reaction center of photosystem I absorbs more light energy and excites electrons. These energized electrons reduce NADP
+, to NADPH. See (
[link] )below for a visual representation of the light-dependent reactions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?