| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In one sense the discrimination in this story is unfortunate in that it prevents the child from acquiring a liking for school that is generalized. But notice that an opposing, more desirable process is happening at the same time: the child is also prevented from acquiring a generalized dislike of school. The fear-producing stimuli from Mr Horrible, in particular, become discriminated from the happiness-producing smiles from you, so the child’s learns to confine his fearful responses to that particular classroom, and does not generalize them to other “innocent” classrooms, including your own. This is still not an ideal situation for the student, but maybe it is more desirable than disliking school altogether.
Instead of focusing on associations between stimuli and responses, operant conditioning focuses on how the effects of consequences on behaviors. The operant model of learning begins with the idea that certain consequences tend to make certain behaviors happen more frequently. If I compliment a student for a good comment during a discussion, there is more of a chance that I will hear comments from the student more often in the future (and hopefully they will also be good ones!). If a student tells a joke to several classmates and they laugh at it, then the student is more likely to tell additional jokes in the future and so on.
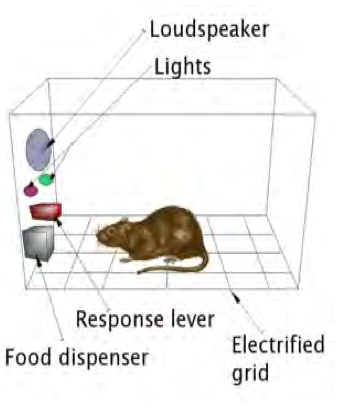
As with classical conditioning, the original research about this model of learning was not done with people, but with animals. One of the pioneers in the field was a Harvard professor named B. F. Skinner, who published numerous books and articles about the details of the process and who pointed out many parallels between operant conditioning in animals and operant conditioning in humans (1938, 1948, 1988). Skinner observed the behavior of rather tame laboratory rats (not the unpleasant kind that sometimes live in garbage dumps). He or his assistants would put them in a cage that contained little except a lever and a small tray just big enough to hold a small amount of food. ( [link] shows the basic set-up, which is sometimes nicknamed a “Skinner box”.) At first the rat would sniff and “putter around” the cage at random, but sooner or later it would happen upon the lever and eventually happen to press it. Presto! The lever released a small pellet of food, which the rat would promptly eat. Gradually the rat would spend more time near the lever and press the lever more frequently, getting food more frequently. Eventually it would spend most of its time at the lever and eating its fill of food. The rat had “discovered” that the consequence of pressing the level was to receive food. Skinner called the changes in the rat’s behavior an example of operant conditioning , and gave special names to the different parts of the process. He called the food pellets the reinforcement and the lever-pressing the operant (because it “operated” on the rat’s environment). See below.
|
Operant → Reinforcement
Press lever → Food pellet |
 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Oneonta epsy 275' conversation and receive update notifications?