| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
DIE SLAAPKAMER
Pas die woorde (woordeskat)
Kies uit die kas die regte woord vir elk van die volgende prentjies. Skryf die woorde langs die prentjie neer.

 |
............................................................................................... | |
 |
................................................................................................ | |
 |
................................................................................................. | |
 |
.............................................................................................. | |
 |
.............................................................................................. | |
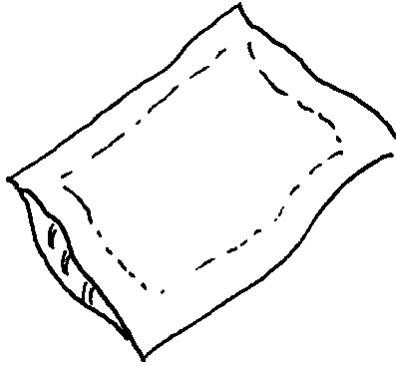 |
.............................................................................................. | |
 |
......................................................................................... | |
 |
.......................................................................................... | |
 |
.......................................................................................... | |
 |
......................................................................................... | |
 |
......................................................................................... | |
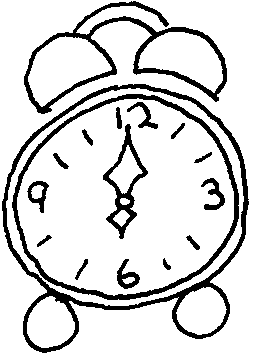 |
......................................................................................... | |
 |
......................................................................................... | |
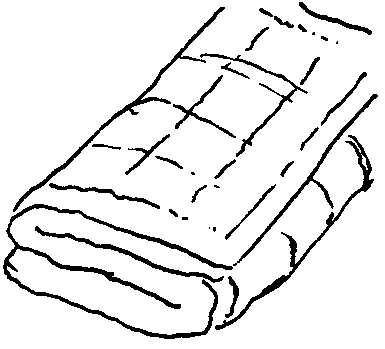 |
.......................................................................................... | |
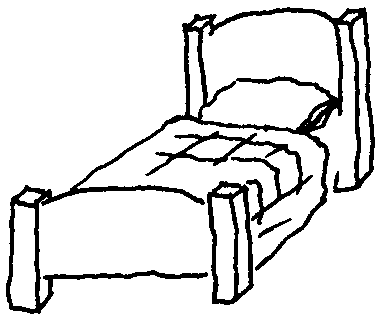 |
.......................................................................................... |
Leer die spelling van die woorde vir ‘n speltoets en skryf jou toetspunt hier neer.
....................................................................................................
Soek die verskil (Mondelinge speletjie)
Hieronder is twee prentjies, A en B, wat van mekaar verskil. Werk saam met 'n maat om die verskille uit te vind. Kies een prent ( A of B ) en hou die ander een toe. Draai jou rug op jou maat. Julle mag nou nie mekaar se prente sien nie.
A moet vir B vertel wat in sy/haar prent is en B moet vir A sê of hy/sy dit ook sien, bv.
A: Op die bedkassie is 'n leeslamp.
B: Ja, op die bedkassie is 'n leeslamp.
A: Op die vloer is 'n matjie.
B: Nee, daar is nie 'n matjie op die vloer nie.
| A |
 |
| B |
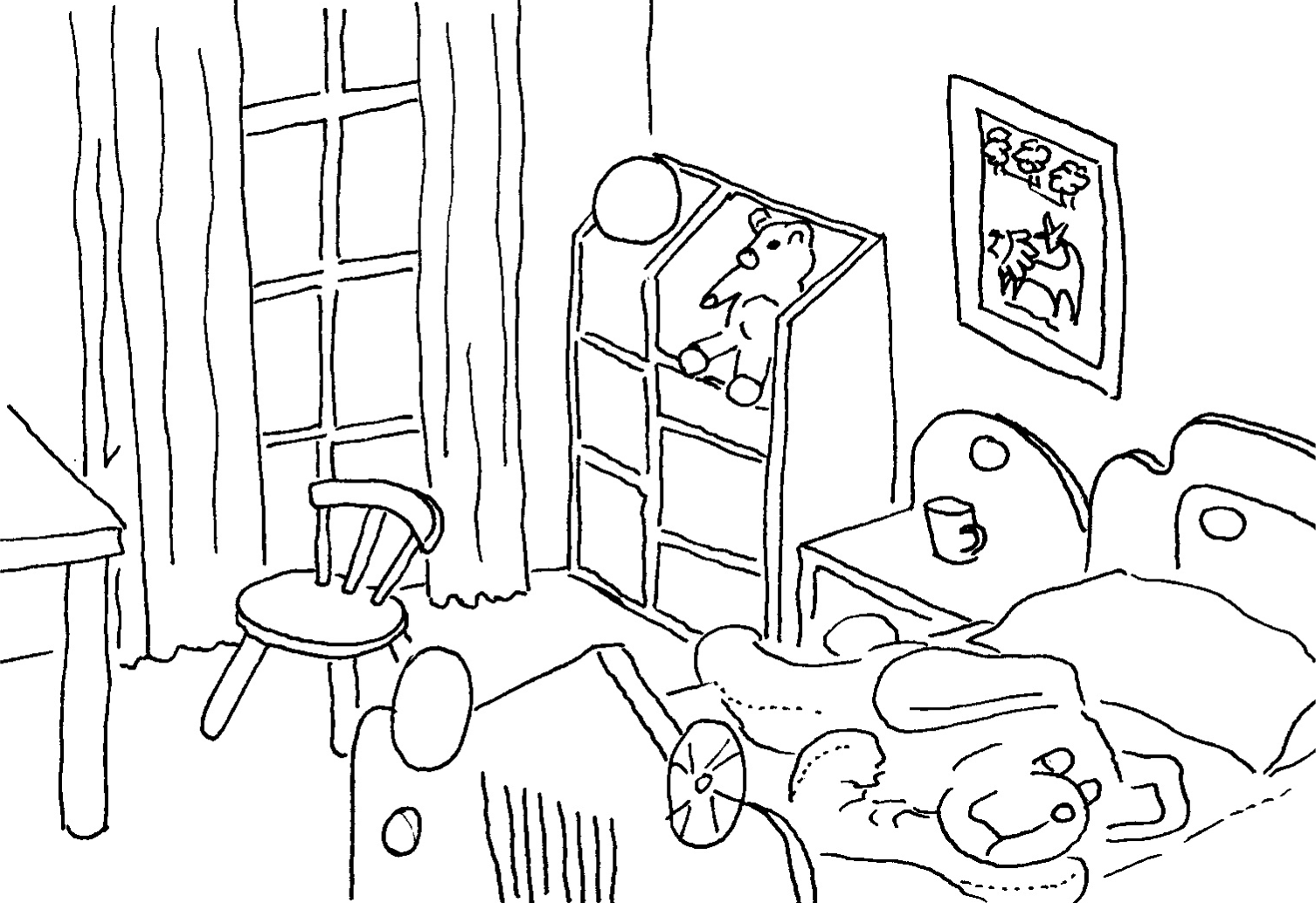 |
Ons het ........................................ verskille gekry.
Bespreek die verskille met ‘n ander groepie en vergelyk jul bevindinge met die res van die klas.
Kom ons maak die bed op (mondeling, aksies en instruksies)
Lees die volgende aksieketting van hoe om 'n bed op te maak en maak jul eie aksies daarby. Die hele klas kan dit saam sê of dit kan in groepe gedoen word.
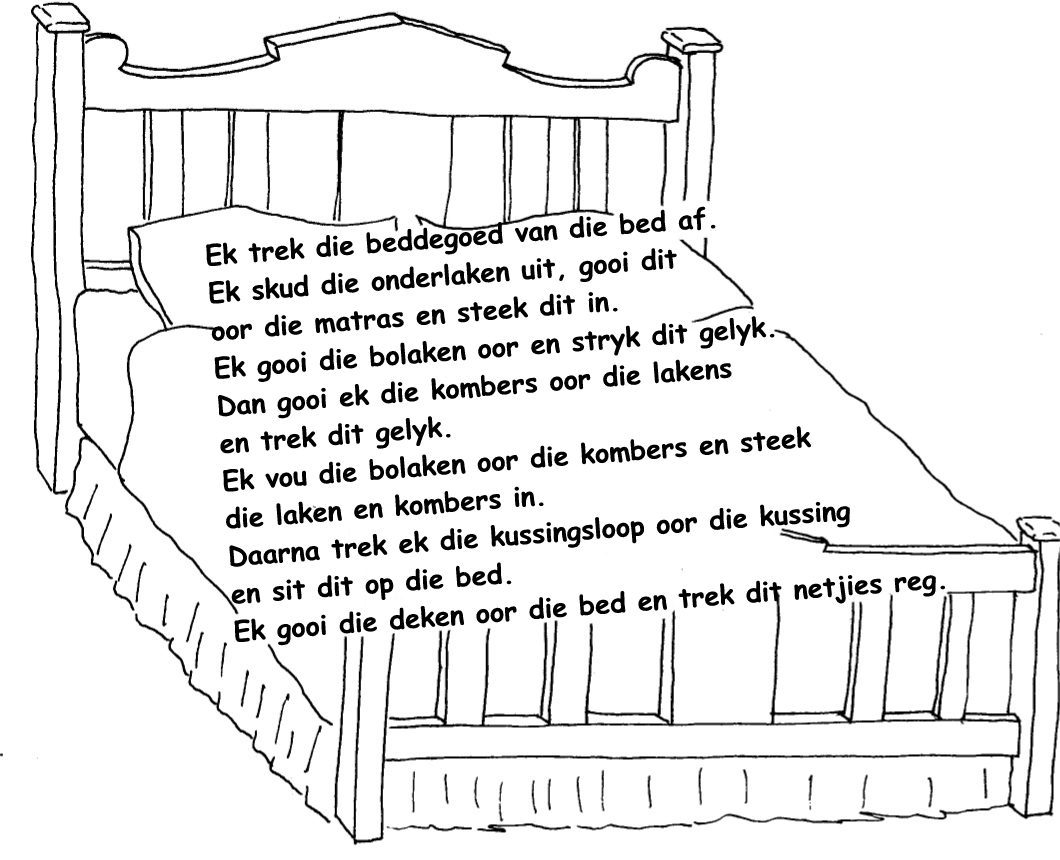
Aktiwiteit 5
Die leerder is in staat om vir inligting en genot te luister en gepas en krities binne ‘n wye verskeidenheid situasies te reageer.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder:
1.2 mondelinge instruksies, aanwysings en beskrywings verstaan:
1.3 verstaan mondelinge beskrywings:
1.3.1 mense, voorwerpe of plekke identifiseer.
Die leerder is in staat om vrymoedig en doeltreffend in gesproke taal binne ‘n wye verskeidenheid situasies te kommunikeer.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder:
2.2 op kultureel gepaste maniere optree:
2.2.1 bekende situasies rolspeel (soos gee aanwysings).
Die leerder is in staat om verskillende soorte feitelike en verbeeldingstekste vir ‘n wye verskeidenheid doeleindes te skryf.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder:
4.5 ontwikkelende kennis gebruik van taalstruktuur en – gebruik:
4.5.2 bekende woorde korrek spel.
Die leerder is in staat om taal vir dink en redeneer te gebruik en inligting vir leer te verkry, verwerk en gebruik.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder:
5.2 taal gebruik om te dink:
5.2.9 met ondersteuning eenvoudige definisies skryf en voorbeelde gee (soos: pas ‘n begrip en sy definisie by ‘n voorbeeld).
Aktiwiteit 1(a)
Hangkas
stoeltjie
kam
borsel
bedlampie
spieël
prente
kussing
laaikas
matjie
spieëltafel
pantoffels
boeke
wekker
laken
kombers
bed

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Afrikaans eerste addisionele taal graad 4' conversation and receive update notifications?