| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
What drives current? We can think of various devices—such as batteries, generators, wall outlets, and so on—which are necessary to maintain a current. All such devices create a potential difference and are loosely referred to as voltage sources. When a voltage source is connected to a conductor, it applies a potential difference that creates an electric field. The electric field in turn exerts force on charges, causing current.
The current that flows through most substances is directly proportional to the voltage applied to it. The German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854) was the first to demonstrate experimentally that the current in a metal wire is directly proportional to the voltage applied :
This important relationship is known as Ohm’s law . It can be viewed as a cause-and-effect relationship, with voltage the cause and current the effect. This is an empirical law like that for friction—an experimentally observed phenomenon. Such a linear relationship doesn’t always occur.
If voltage drives current, what impedes it? The electric property that impedes current (crudely similar to friction and air resistance) is called resistance . Collisions of moving charges with atoms and molecules in a substance transfer energy to the substance and limit current. Resistance is defined as inversely proportional to current, or
Thus, for example, current is cut in half if resistance doubles. Combining the relationships of current to voltage and current to resistance gives
This relationship is also called Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law in this form really defines resistance for certain materials. Ohm’s law (like Hooke’s law) is not universally valid. The many substances for which Ohm’s law holds are called ohmic . These include good conductors like copper and aluminum, and some poor conductors under certain circumstances. Ohmic materials have a resistance that is independent of voltage and current . An object that has simple resistance is called a resistor , even if its resistance is small. The unit for resistance is an ohm and is given the symbol (upper case Greek omega). Rearranging gives , and so the units of resistance are 1 ohm = 1 volt per ampere:
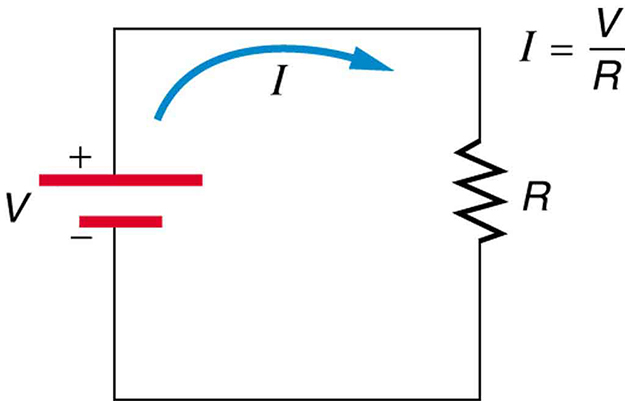
[link] shows the schematic for a simple circuit. A simple circuit has a single voltage source and a single resistor. The wires connecting the voltage source to the resistor can be assumed to have negligible resistance, or their resistance can be included in .
What is the resistance of an automobile headlight through which 2.50 A flows when 12.0 V is applied to it?
Strategy
We can rearrange Ohm’s law as stated by and use it to find the resistance.
Solution
Rearranging and substituting known values gives
Discussion
This is a relatively small resistance, but it is larger than the cold resistance of the headlight. As we shall see in Resistance and Resistivity , resistance usually increases with temperature, and so the bulb has a lower resistance when it is first switched on and will draw considerably more current during its brief warm-up period.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?