| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For the point C outside the conductor, the current inside the loop is I.
In this case, current is distributed across the cross section uniformly. In order to apply Ampere’s law, we consider three imaginary circles containing these points separately with their centers lying on the axis of cylinder such that their planes are at right angles to the cylinder. Let the total current through the conductor is I.
Magnetic field due to a long cylindrical conductor with uniform current density

For the point A inside the conductor, the current inside the loop is not zero. Since current is distributed over the cross section area uniformly, the current through the loop area is proportionately smaller and is given by :
Now,
For the point B just outside the conductor, the current inside the loop is I.
For the point C outside the conductor, the current inside the loop is I.
Problem : The current density varies within a long cylindrical wire of radius “R” as J=kr where “r” is linear distance from the center in the perpendicular cross section of wire. Find the magnetic field at a distance r= R/2 and at a point outside the wire.
Solution : In order to find the current within the conductor, we consider an annular ring of infinitesimally small thickness “dr”. The current through the small cross section of annular ring is :
Magnetic field due to a long cylindrical conductor with non-uniform current density
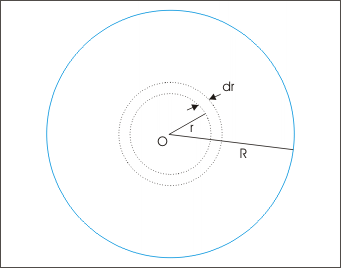
Integrating between r = 0 and r =R/2, the current inside the circular loop of radius R/2 is,
Applying Ampere’s law about a loop of radius R/2,
For additional examples, see Ampere's law(exercise) : Problem 5,6,7 and 9
A solenoid is a tightly wound helical coil. It works as a magnet when current is passed through the coil. We may treat a solenoid as the aggregation of large numbers of circular current aligned about a common axis. It tends to reinforce magnetic field due to each of the circular coil, resulting into a device to produce magnetic field. An ideal solenoid has infinite length. A long coil approximates an ideal solenoid. The consideration here is valid for even short solenoid for points which are well inside the coil.
Solenoid

The current in left end coil is clockwise and serves as south end of solenoid i.e. end through which magnetic field enters the solenoid. On the other hand, the current in the right end coil is anticlockwise and serves as north end of solenoid i.e. end through which magnetic field exits the solenoid. The magnetic fields between two adjacent coils at the periphery (edge) cancel each other. The magnetic field outside solenoid is nearly zero or comparatively much weaker to be considered to be zero. The field inside the solenoid is uniform. The magnetic field at the ends of solenoid, however, spreads out. The nature of magnetic field of a solenoid is similar to magnetic field due to a bar magnet.
Magnetic field due to a solenoid

We draw a rectangular Ampere loop ACDEA as shown in the figure. The directions of currents at the edges are shown by filled circle for currents coming out of the plane of drawing and by cross for currents going into the plane of drawing. We carry out the integration in anticlockwise direction such that currents coming out of the plane of drawing are considered positive.
Magnetic field due to a solenoid

Applying Ampere’s law,
We see that magnetic filed is either perpendicular or there is no magnetic field in transverse directions from C to D and from E to A. For these conditions, the integral along these paths are zero. Further, the line segment DE falls in the region where magnetic field is zero. Thus, all three integrals except the first on the right hand side are equal to zero.
The total current through the loop is numbers of times the wire crosses the plane of drawing. If “n” be the numbers of turns per unit length, then total current is “na”. Hence,
The magnetic field is proportional to the current and numbers of turns per unit length of solenoid. Importantly, it does not depend on the radius of coil.
For illustration, see Ampere's law(exercise) : Problem 8 .
A toroid is solenoid bent along a circular path in the shape of a doughnut. By symmetry, the magnetic field is circular inside the toroid and is zero outside it. It is also constant on a circular loop of radius “r” drawn inside the toroid being equidistant from the center of doughnut. The total current passing through Ampere loop is NI where N is the total numbers of turns. Applying Ampere’s law, we have :
Magnetic field due to a toroid

The magnetic field and line element vectors are in the same direction. Hence,
It is important to observe that magnetic field inside the toroid is not constant across the cross-section. It is inversely proportional to “r”. It depends upon the linear distance as we move from the interior side to exterior side. We may also write this expression in terms of numbers of turns per unit length as :
and
But this form is not advisable as it conceals the non-uniform nature of magnetic field inside the toroid. It is easy to find the direction of magnetic field. We orient the fingers of right hand in the direction of current along the turn of coil. Then, the extended thumb gives the direction of magnetic field.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Electricity and magnetism' conversation and receive update notifications?