| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Distance (m) | Time (s) | ||
| 1 | 2 | Ave. | |
| 0 | |||
| 0,5 | |||
| 1,0 | |||
| 1,5 | |||
| 2,0 | |||
| 2,5 | |||
| 3,0 |
The final situation we will be studying is motion at constant acceleration. We know that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. So, if we have a constant acceleration, this means that the velocity changes at a constant rate.
Let's look at our first example of Lesedi waiting at the taxi stop again. A taxi arrived and Lesedi got in. The taxi stopped at the stop street and then accelerated as follows: After the taxi covered a distance of , after it covered , after it covered and after it covered . The taxi is covering a larger distance every second. This means that it is accelerating.

To calculate the velocity of the taxi you need to calculate the gradient of the line at each second:
From these velocities, we can draw the velocity-time graph which forms a straight line.
The acceleration is the gradient of the vs. graph and can be calculated as follows:
The acceleration does not change during the motion (the gradient stays constant). This is motion at constant or uniform acceleration.
The graphs for this situation are shown in [link] .
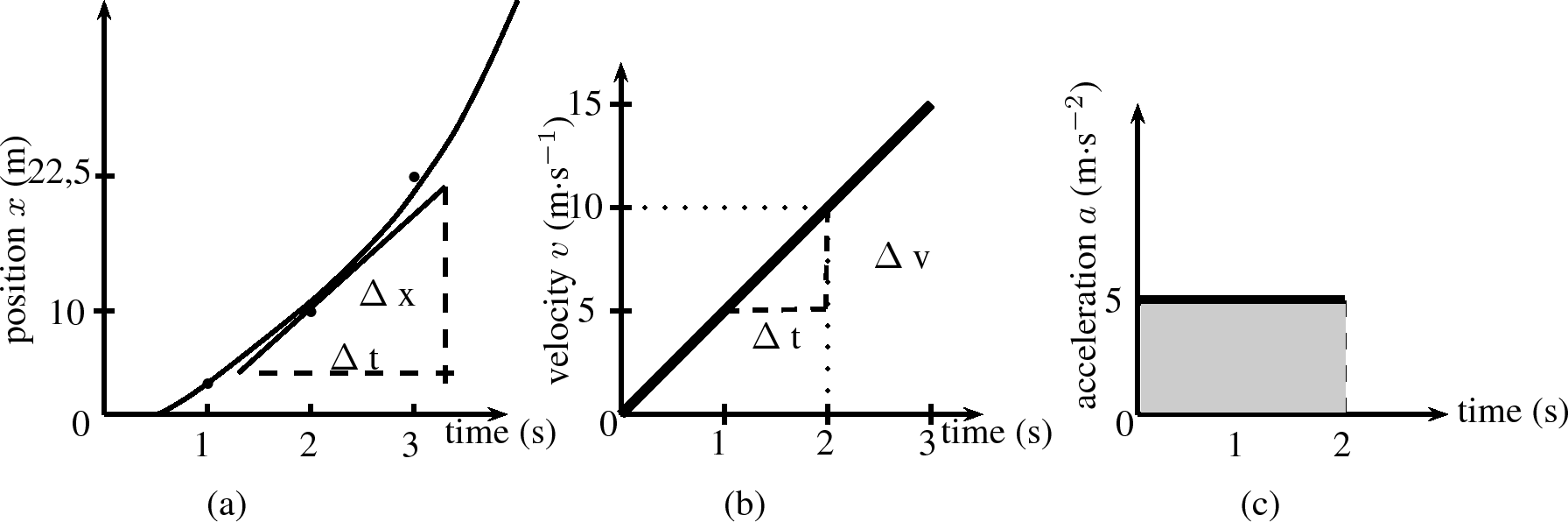
Just as we used velocity vs. time graphs to find displacement, we can use acceleration vs. time graphs to find the velocity of an object at a given moment in time. We simply calculate the area under the acceleration vs. time graph, at a given time. In the graph below, showing an object at a constant positive acceleration, the increase in velocity of the object after 2 seconds corresponds to the shaded portion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?