| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Review the process of meiosis, observing how chromosomes align and migrate, at Meiosis: An Interactive Animation .
In some species, cells enter a brief interphase, or interkinesis , before entering meiosis II. Interkinesis lacks an S phase, so chromosomes are not duplicated. The two cells produced in meiosis I go through the events of meiosis II in synchrony. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids within the two daughter cells separate, forming four new haploid gametes. The mechanics of meiosis II is similar to mitosis, except that each dividing cell has only one set of homologous chromosomes. Therefore, each cell has half the number of sister chromatids to separate out as a diploid cell undergoing mitosis.
If the chromosomes decondensed in telophase I, they condense again. If nuclear envelopes were formed, they fragment into vesicles. The centrosomes that were duplicated during interkinesis move away from each other toward opposite poles, and new spindles are formed.
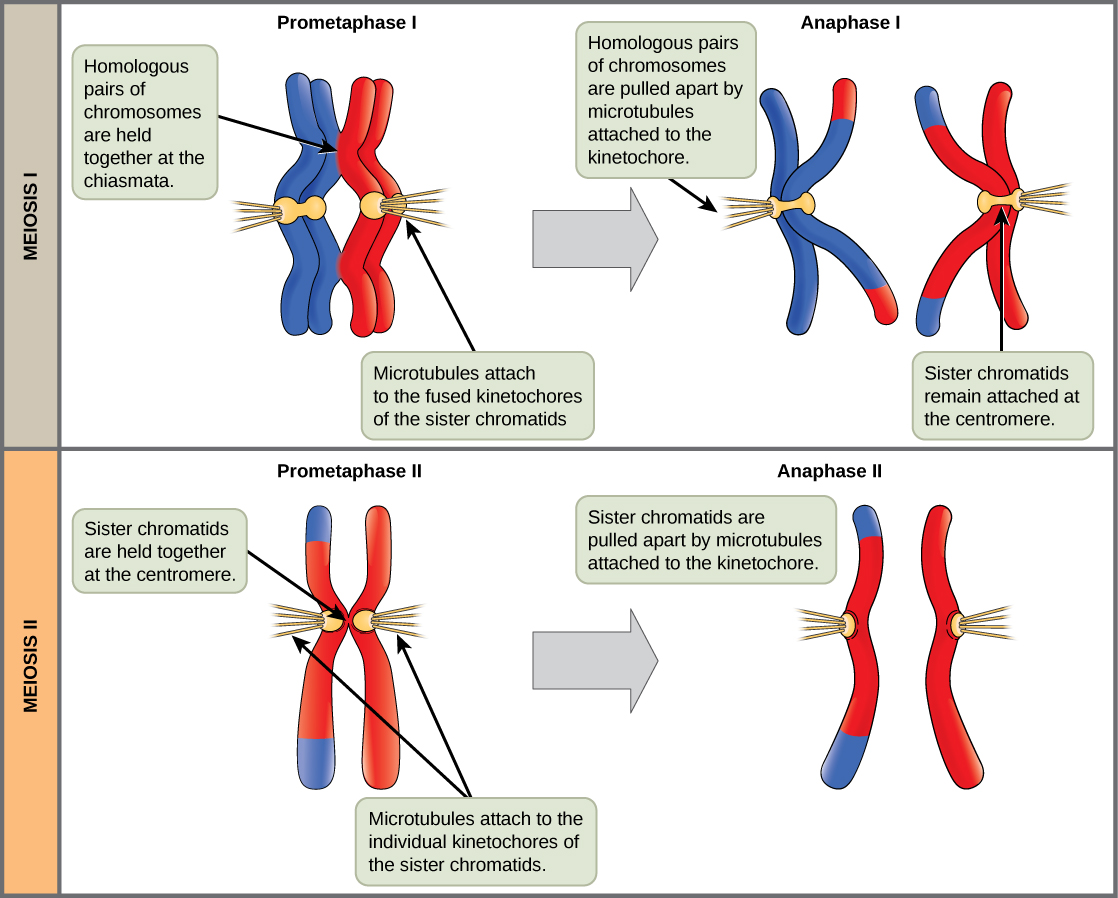
The nuclear envelopes are completely broken down, and the spindle is fully formed. Each sister chromatid forms an individual kinetochore that attaches to microtubules from opposite poles.
The sister chromatids are maximally condensed and aligned at the equator of the cell.
The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the kinetochore microtubules and move toward opposite poles. Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate the cell.
The chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense. Nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes. Cytokinesis separates the two cells into four unique haploid cells. At this point, the newly formed nuclei are both haploid. The cells produced are genetically unique because of the random assortment of paternal and maternal homologs and because of the recombining of maternal and paternal segments of chromosomes (with their sets of genes) that occurs during crossover. The entire process of meiosis is outlined in [link] .
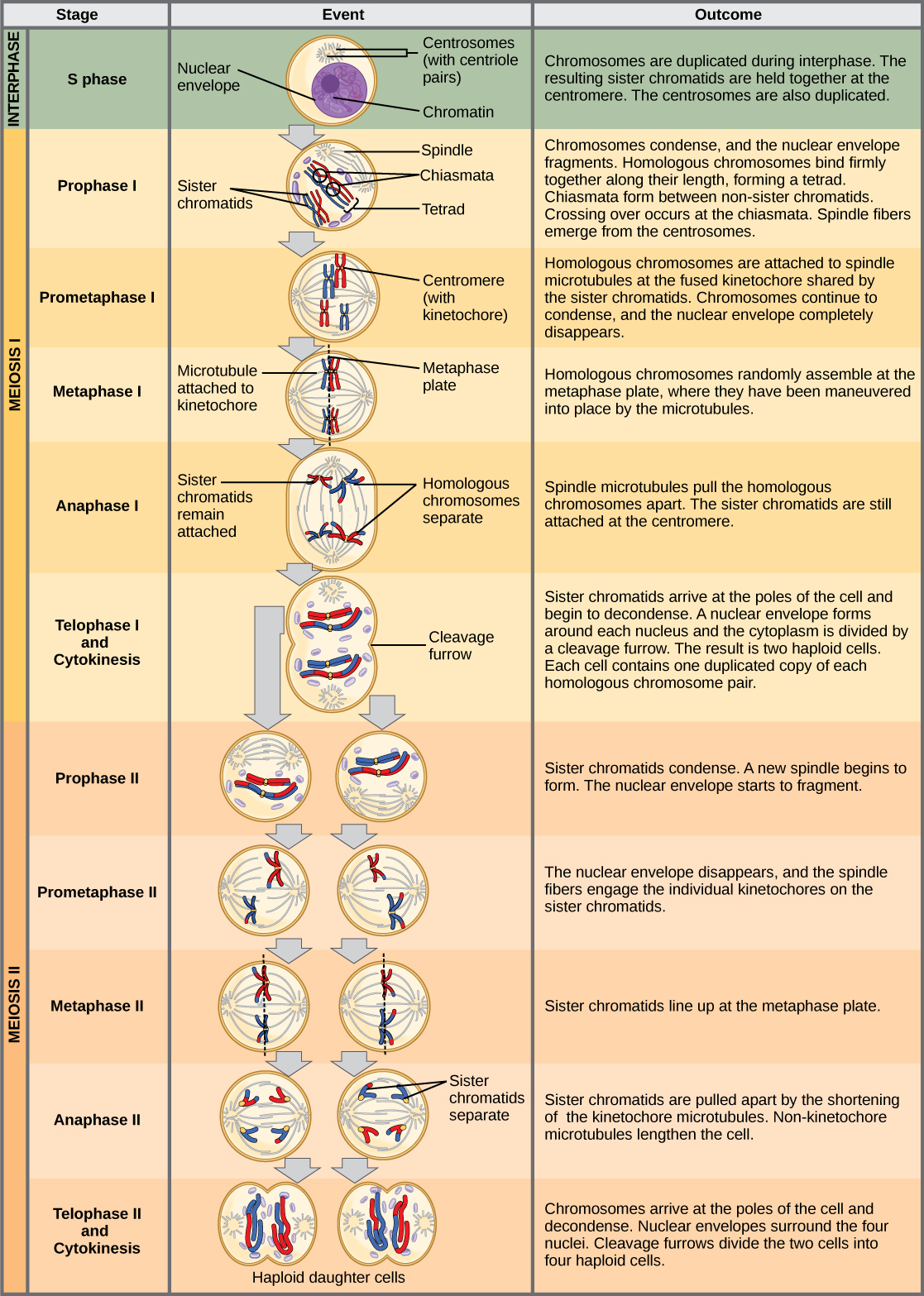
Mitosis and meiosis are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes ( [link] ). Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei that are usually partitioned into two new cells. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division are genetically identical to the original nucleus. They have the same number of sets of chromosomes, one set in the case of haploid cells and two sets in the case of diploid cells. In most plants and all animal species, it is typically diploid cells that undergo mitosis to form new diploid cells. In contrast, meiosis consists of two nuclear divisions resulting in four nuclei that are usually partitioned into four new cells. The nuclei resulting from meiosis are not genetically identical and they contain one chromosome set only. This is half the number of chromosome sets in the original cell, which is diploid.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?