| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Because GWAS looks for associations between genes and disease, these studies provide data for other research into causes, rather than answering specific questions themselves. An association between a gene difference and a disease does not necessarily mean there is a cause-and-effect relationship. However, some studies have provided useful information about the genetic causes of diseases. For example, three different studies in 2005 identified a gene for a protein involved in regulating inflammation in the body that is associated with a disease-causing blindness called age-related macular degeneration. This opened up new possibilities for research into the cause of this disease. A large number of genes have been identified to be associated with Crohn’s disease using GWAS, and some of these have suggested new hypothetical mechanisms for the cause of the disease.
Pharmacogenomics involves evaluating the effectiveness and safety of drugs on the basis of information from an individual's genomic sequence. Personal genome sequence information can be used to prescribe medications that will be most effective and least toxic on the basis of the individual patient’s genotype. Studying changes in gene expression could provide information about the gene transcription profile in the presence of the drug, which can be used as an early indicator of the potential for toxic effects. For example, genes involved in cellular growth and controlled cell death, when disturbed, could lead to the growth of cancerous cells. Genome-wide studies can also help to find new genes involved in drug toxicity. The gene signatures may not be completely accurate, but can be tested further before pathologic symptoms arise.
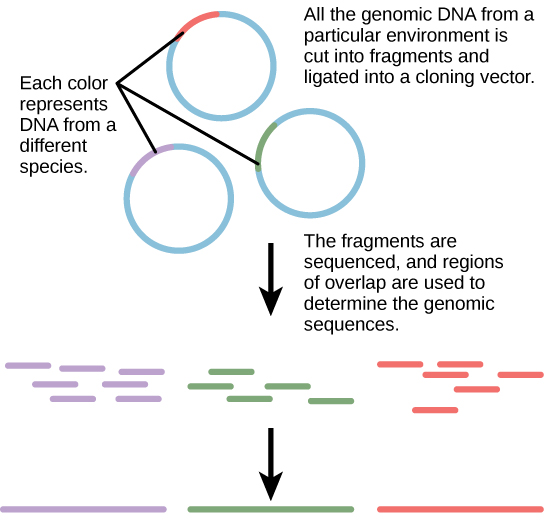
Traditionally, microbiology has been taught with the view that microorganisms are best studied under pure culture conditions, which involves isolating a single type of cell and culturing it in the laboratory. Because microorganisms can go through several generations in a matter of hours, their gene expression profiles adapt to the new laboratory environment very quickly. On the other hand, many species resist being cultured in isolation. Most microorganisms do not live as isolated entities, but in microbial communities known as biofilms. For all of these reasons, pure culture is not always the best way to study microorganisms. Metagenomics is the study of the collective genomes of multiple species that grow and interact in an environmental niche. Metagenomics can be used to identify new species more rapidly and to analyze the effect of pollutants on the environment ( [link] ). Metagenomics techniques can now also be applied to communities of higher eukaryotes, such as fish.
Knowledge of the genomics of microorganisms is being used to find better ways to harness biofuels from algae and cyanobacteria. The primary sources of fuel today are coal, oil, wood, and other plant products such as ethanol. Although plants are renewable resources, there is still a need to find more alternative renewable sources of energy to meet our population’s energy demands. The microbial world is one of the largest resources for genes that encode new enzymes and produce new organic compounds, and it remains largely untapped. This vast genetic resource holds the potential to provide new sources of biofuels ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?