| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
INTRODUCTION
The Grade 1 educator needs to determine whether the learners have attended a pre-primary class or not. For the learners who have not attended a pre-primary, Modules 1 and 2 may have to be adapted to include more activities so as to reinforce the vocabulary and concepts in these modules. For the learners who have attended pre-primary schools, Modules 1 and 2 will serve as revision exercises giving the educator a clear picture as to what they know.
TIME SCHEDULE
Two modules have been designed for each term. The educator may however find that the fast workers will complete the modules in less time than the slower workers. The educator should feel free to extend the number range for the learners who are ready for it. The minimum requirements for the slow learners are Modules 1 to 7.
Critical and developmental outcomes:
The learners must be able to:
1. identify and solve problems and make decisions using critical and creative thinking;
2. work effectively with others as members of a team, group, organisation and community;
3. organise and manage themselves and their activities responsibly and effectively;
4. collect, analyse, organise and critically evaluate information;
5. communicate effectively using visual, symbolic and/or language skills in various modes;
6. use science and technology effectively and critically, showing responsibility towards the environment and the health of others;
7. demonstrate an understanding of the world as a set of related systems by recognising that problem-solving contexts do not exist in isolation;
8. reflect on and explore a variety of strategies to learn more effectively;
9. participate as responsible citizens in the life of local, national, and global communities;
10. be culturally and aesthetically sensitive across a range of social contexts;
11. explore education and career opportunities; and
12. develop entrepreneurial opportunities.
Activities around signs of spring help learners to understand:

4, 8, …………, …………, 20, …………, …………, 32, …………, 40.
| LO 1.7 | LO 1.8 | LO 2.2 |



_ _ _c

_ _ _c

_ _ _c

_ _ _c
| LO 1.5 |
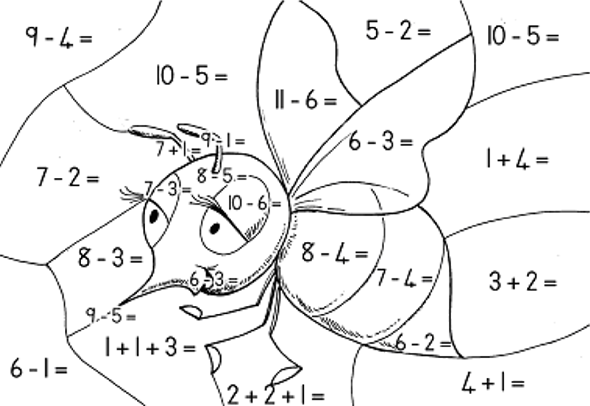
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 8 |
| purple | black | yellow | red | brown |


How many flowers? ……………………………………………..
Double them …………………………………………………..
| LO 1.2 | LO 1.8 | LO 1.9 |


| 2 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 8 | |
| +2 | ||||||
| +3 | ||||||
| +4 |
| 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7 | 5 | |
| -2 | ||||||
| -3 | ||||||
| -4 |
| LO 1.8 | LO 1.9 |



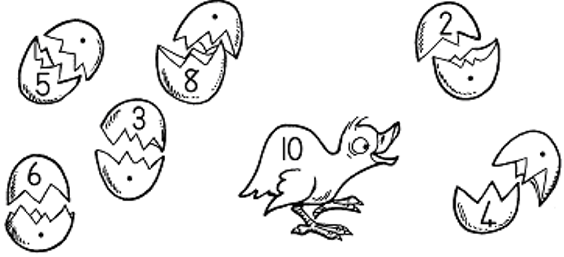
| LO 1.8 | LO 1.9 |

10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
10 = ……………………. + …………………….
| LO 1.2 | LO 1.8 |

12 = 10 + ……………………………..
13 = 10 + ……………………………..
14 = 10 + ……………………………..
15 = 10 + ……………………………..
16 = 10 + ……………………………..
17 = 10 + ……………………………..
18 = 10 + ……………………………..
19 = 10 + ……………………………..
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| +10 |
| LO 1.9 | LO 4.2 |
Learning Outcome 1: NUMBERS, OPERATIONS AND RELATIONSHIPS: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner counts forward and backwards in;
Assessment Standard 1.5: We know this when the learner solves money problems involving totals and change in rands and cents;
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner can perform calculations, using appropriate symbols, to solve problems;
Assessment Standard 1.8: We know this when the learner performs mental calculations involving addition and subtraction for numbers to at least 10;
Assessment Standard 1.9: We know this when the learner uses techniques.
Learning Outcome 2: PATTERNS, FUNCTIONS AND ALGEBRA: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.2: We know this when the learner copies and extends simple number sequences to at least 100;
Learning Outcome 4: MEASUREMENT : The learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts.
Assessment Standard 4.2: We know this when the learner compares events in terms of the length of time they take (longer, shorter, faster, slower).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?