| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Definition 2 A Michell Topology of order consists of Michell spirals of order less than or equal to and their conjugate spirals where [link] and [link] hold.
A force applied to a node can be represented by the vector applied to the node and written in complex form as
where
and is the angle at which the external force is applied, measured from the radial line to node .
At node , the forces along directions , respectively, have magnitudes . Therefore, the sum of forces at node yields
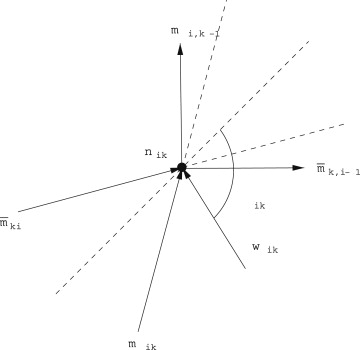
Multiplying [link] by the vector gives
Because both the real and imaginary parts of the above equation must be zero,
Define a vector which contains forces in all members that lie within the radii and . That is,
Define a vector such that
Theorem 1 Let a truss be arranged according to the Michell topology of order , satisfying the conditions in the definitions, having external forces applied at the nodes with and . Let contain the forces(normalized by the member length) in all members within the band of members between radii and . Then the forces propagate from one band to the next according to the linear recursive equation for some matrices and .
If , then one member of the truss is in compression while the other is in tension, so the truss is said to be bending.
Theorem 2 Let a truss be arranged according to the Michell topology of order satisfying [link] and with and given by [link] . Assume the only force applied on the truss is at node . If
then the forces at all nodes satisfy
Furthermore, if
then for all , . Otherwise, if
then for all , .
First, take the case where . In this case, is the only node at which external forces are applied:
In the case when , there are three cases of interest. The first is when . Then and
which implies and , or, in other words, that both members of the truss are in tension.
The second case is when . A similar analysis shows that and so both members of the truss are in compression.
Lastly, when then , indicating that one member of the truss is in tension and the other in compression, so the truss is said to be bending.
Now, consider the case where and assume that so that and (the opposite case is handled similarly). Consider the node . In the force diagram, by assumption, hence because is at the lower boundary of the truss. Repeat the analysis from before for the fictitious force . Because the truss has , , so that and . The same idea, applied to all nodes on the upper boundary with , proves that and for all .
The analysis at node is similar. Repeat the above analysis for a fictitious force . The vector has a negative sign because the angle is measured clockwise, so the vector needs to be flipped to get the same angle as before. Therefore, for all nodes with , and for all .
Continuing on, for the node , use a fictitious force . Because , one can conclude that to get that and , and continuing in this fashion gives and for all .
The last type of node to consider is an interior node of the form where . At the node create the fictitious force . The assumption that leads to the conclusion that , yielding and . Therefore, when ,
A similar procedure for yields
Let , denote the yield stress of the material used to construct the th member, , loaded with force density and with constant cross section area . To avoid material failure, the force density at any given member should satisfy
with equality holding in minimal volume structures. Some algebra yields
where is the volume of each member. Therefore, the total volume of a structure, , is
Let and be the bar and string vectors for the th compressive or tensile member in a structure with bars and strings. Therefore , where
Assuming that all bars are the same material, for all . Likewise, if all strings are made of the same material, then for all . Hence
so that
Now, let be defined by
From [link] and [link] , it is true for a structure in static equilibrium that
Let and Therefore
Thus
Assuming that , we get that
which is consistent with [link] . This implies that minimization of is independent of the choice of material properties, and depends only on the variable topology.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Michell trusses study, rice u. nsf vigre group, summer 2013' conversation and receive update notifications?