| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Our research revolves around devising an algorithm based on CFTP [link] to exactly sample from SYD's, , that fit in an a b box according to the probability distribution given by equation [link] . We found two algorithms. The first algorithm, explained in "Exact Sampling of SYD's in an a×b Box Greater Than or Equal to a Fixed YD" , exactly samples from SYD's that fit in an a b box where is greater than or equal to a fixed YD . The second algorithm, explained in "Exact Sampling of SYD's in an a×b Box Greater Than or Equal to One of Two Fixed YD's" exactly samples from SYD's that fit in an a b box where is greater than or equal to or , where and are fixed YD's.
Propp and Wilson call their algorithm for exactly sampling YD's the monotone Monte Carlo [link] algorithm. This algorithm involves Markov chains and a process called Coupling from the Past.
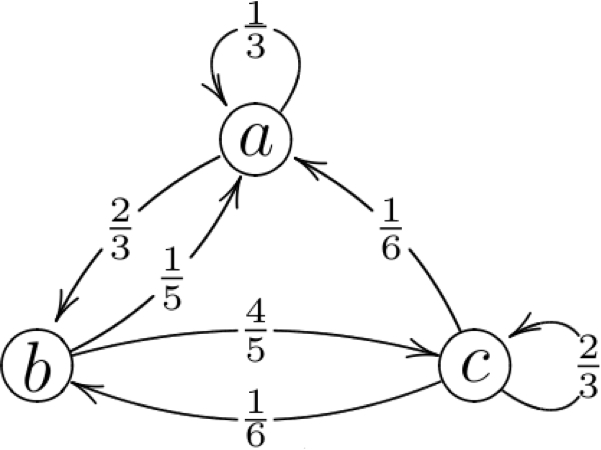
A Markov chain (“MC") consists of a finite number of states (which may be represented by circles) and paths between states with assigned probabilities (which may be represented by arrows). For example, see [link] . The probabilities on all arrows leaving a state should add to one. Consider a walk on the set of states of a MC where each step follows an arrow in it. Choosing which state to go to next depends only on your current state and the probabilities on the arrows leaving your current state. In other words, each step is independent of all steps that happened before you landed on your current state (the “history" of that state).
In a forward Monte Carlo Markov chain simulation, one starts with an initial distribution on the state space and runs the MC. The probability distribution on a state set changes with each step of the MC. It is known that if a MC is ergodic (aperiodic, positive recurrent, and irreducible), then if the number of steps you follow the MC into the future is taken to infinity, the probability distribution approaches what is called the steady state distribution. The steady state distribution, also called the stationary distribution, is the probability distribution that does not change after one step of the MC. The MC will approach its stationary distribution regardless of the distribution you start with, and if a MC is ergodic, it has a unique stationary distribution.
To use a MC to sample from YD's or SYD's, we simply define our state set to consist of the finite number of YD's or SYD's that fit in an a b box and assign probabilities to arrows from state to state in such a way that our MC is ergodic.
Instead of forward simulation, Propp and Wilson simulate from the past and apply Coupling from the Past (“CFTP") [link] . CFTP works with ergodic MC's that have their stationary distribution equal to the probability distribution you wish to sample the states with. CFTP is executed in the following manner.
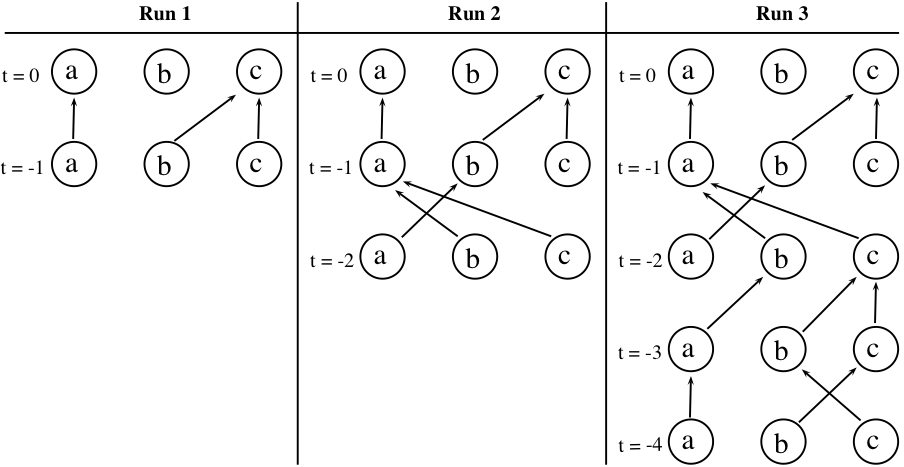
Start with at time . Select one arrow leading from each state at time (according to the probabilities assigned to the arrows) to some state at time . Let be the number of states in your state set. Thus you must select arrows at each step. Each arrow indicates which path will be followed from time to time from the state the arrow leaves. You have completed one “run" of the CFTP algorithm. Now analyze the paths: do they all lead to the same state at time ?If they do, this is called “coalescence". If not, conduct another run of CFTP as stated in the next paragraph, making sure to “save" the arrows you chose in this step. If all histories coalesce, output the state they return at .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?