| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
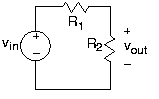
At every node, the sum of all currents entering or leaving a node must equal zero. What this law means physically is that chargecannot accumulate in a node; what goes in must come out. In the example, [link] , below we have a three-node circuit and thus have three KCLequations. Note that the current entering a node is the negative of the current leaving the node.
Given any two of these KCL equations, we can find the other by adding or subtracting them. Thus, one of them is redundantand, in mathematical terms, we can discard any one of them. The convention is to discard the equation for the(unlabeled) node at the bottom of the circuit.

In writing KCL equations, you will find that in an -node circuit, exactly one of them is always redundant. Can you sketch a proof of whythis might be true? Hint: It has to do with the fact that charge won't accumulate in one place on its own.
KCL says that the sum of currents entering or leaving a node must be zero. If we consider two nodes together as a"supernode", KCL applies as well to currents entering the combination. Since no currents enter an entire circuit,the sum of currents must be zero. If we had a two-node circuit, the KCL equation of one must be the negative of the other, We can combine all but one node in a circuit into a supernode; KCL for the supernodemust be the negative of the remaining node's KCL equation. Consequently, specifying KCL equations always specifies the remaining one.
The voltage law says that the sum of voltages around every closed loop in the circuit must equal zero. A closed loop hasthe obvious definition: Starting at a node, trace a path through the circuit that returns you to the origin node. KVLexpresses the fact that electric fields are conservative: The total work performed in moving a test charge around a closedpath is zero. The KVL equation for our circuit is In writing KVL equations, we follow the convention that an element's voltage enters with a plus sign when traversing theclosed path, we go from the positive to the negative of the voltage's definition.
For the example circuit , we have three v-i relations, two KCL equations, and one KVL equation for solving for the circuit's six voltages andcurrents. We have exactly the right number of equations! Eventually, we will discover shortcuts for solving circuit problems; for now,we want to eliminate all the variables but and determine how it depends on and on resistor values. The KVL equation can be rewritten as . Substituting into it the resistor's v-i relation, we have . Yes, we temporarily eliminate the quantity we seek. Though notobvious, it is the simplest way to solve the equations. One of the KCL equations says , which means that . Solving for the current in the output resistor, we have . We have now solved the circuit : We have expressed one voltage or current in terms of sources andcircuit-element values. To find any other circuit quantities, we can back substitute this answer into our original equations orones we developed along the way. Using the v-i relation for the output resistor, we obtain the quantity we seek.
Referring back to [link] , a circuit should serve some useful purpose. What kind ofsystem does our circuit realize and, in terms of element values, what are the system's parameter(s)?
The circuit serves as an amplifier having a gain of .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?