| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In a normal distribution a student who scores the mean value is always in the fiftieth percentile because the mean and median are the same. A score of +1 standard deviation above the mean (e.g. 115 in the example above) is the 84 per cent tile (50 per cent and 34 per cent of the scores were below 115). In [link] we represent the percentile equivalents to the normal curve and we also show standard scores. 1
A standard score expresses performance on a test in terms of standard deviation units above of below the mean (Linn&Miller, 2005). There are a variety of standard scores:
Z-score: One type of standard score is a z-score, in which the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. This means that a z-score tells us directly how many standard deviations the score is above or below the mean. For example, if a student receives a z score of 2 her score is two standard deviations above the mean or the eighty-fourth percentile. A student receiving a z score of -1.5 scored one and one half deviations below the mean. Any score from a normal distribution can be converted to a z score if the mean and standard deviation is known. The formula is:
So, if the score is 130 and the mean is 100 and the standard deviation is 15 then the calculation is:
If you look at [link] Exhibit 9 you can see that this is correct—a score of 130 is 2 standard deviations above the mean and so the z score is 2.
T-score: A T-score has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10. This means that a T-score of 70 is two standard deviations above the mean and so is equivalent to a z-score of 2.
Stanines: Stanines (pronounced staynines) are often used for reporting students’ scores and are based on a standard nine point scale and with a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 2. They are only reported as whole numbers and Figure 11-10 shows their relation to the normal curve.
A grade equivalent score provides an estimate of test performance based on grade level and months of the school year (Popham, 2005, p. 288). A grade equivalent score of 3.7 means the performance is at that expected of a third grade student in the seventh month of the school year. Grade equivalents provide a continuing range of grade levels and so can be considered developmental scores. Grade equivalent scores are popular and seem easy to understand however they are typically misunderstood. If, James, a fourth grade student, takes a reading test and the grade equivalent score is 6.0; this does not mean that James can do sixth grade work . It means that James performed on the fourth grade test as a sixth grade student is expected to perform. Testing companies calculate grade equivalents by giving one test to several grade levels. For example a test designed for fourth graders would also be given to third and fifth graders. The raw scores are plotted and a trend line is established and this is used to establish the grade equivalents. Note that in Error: Reference source not found the trend line extends beyond the grades levels actually tested so a grade equivalent above 5.0 or below 3.0 is based solely on the estimated trend lines.
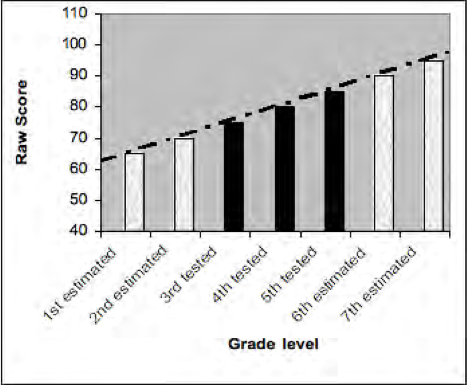
Grade equivalent scores also assume that the subject matter that is being tested is emphasized at each grade level to the same amount and that mastery of the content accumulates at a mostly constant rate (Popham, 2005). Many testing experts warn that grade equivalent scores should be interpreted with considerable skepticism and that parents often have serious misconceptions about grade equivalent scores. Parents of high achieving students may have an inflated sense of what their child’s levels of achievement.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Educational psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?