| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Through discussion of the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem and Whittaker-Shannon reconstruction formula, it has already been shown that a continuous time signal can be reconstructed from its samples at rate via the sinc interpolation filter if . Now, this module will investigate a problematic phenomenon, called aliasing, that can occur if this sufficient condition for perfect reconstruction does not hold. When aliasing occurs the spectrum of the samples has different form than the original signal spectrum, so the samples cannot be used to reconstruct the original signal through Whittaker-Shannon interpolation.
Aliasing occurs when each period of the spectrum of the samples does not have the same form as the spectrum of the original signal. Given a continuous time signals with continuous time Fourier transform , recall that the spectrum of sampled signal with sampling period is given by
As has already been mentioned several times, if is bandlimited to then each period of has the same form as . However, if is not bandlimited to , then the can overlap and sum together. This is illustrated in [link] in which sampling above the Nyquist frequency produces a samples spectrum of the same shape as the original signal, but sampling below the Nyquist frequency produces a samples spectrum with very different shape. Whittaker-Shannon interpolation of each of these sequences produces different results. The low frequencies not affected by the overlap are the same, but there is noise content in the higher frequencies caused by aliasing. Higher frequency energy masquerades as low energy content, a highly undesirable effect.

Unlike when sampling above the Nyquist frequency, sampling below the Nyquist frequency does not yield an injective (one-to-one) function from the bandlimited continuous time signals to the discrete time signals. Any signal with spectrum which overlaps and sums to samples to . It should be intuitively clear that there are very many bandlimited signals that sample to a given discrete time signal below the Nyquist frequency, as is demonstrated in [link] . It is quite easy to construct uncountably infinite families of such signals.
Aliasing obtains it name from the fact that multiple, in fact infinitely many, bandlimited signals sample to the same discrete sequence if . Thus, information about the original signal is lost in this noninvertible process, and these different signals effectively assume the same identity, an “alias”. Hence, under these conditions the Whittaker-Shannon interpolation formula will not produce a perfect reconstruction of the original signal but will instead give the unique bandlimited signal that samples to the discrete sequence.
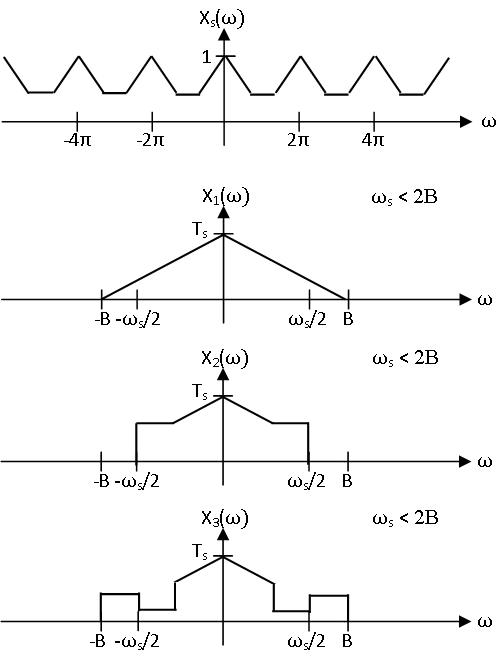
Aliasing, essentially the signal processing version of identity theft, occurs when each period of the spectrum of the samples does not have the same form as the spectrum of the original signal. As has been shown, there can be infinitely many bandlimited signals that sample to a given discrete time signal at a rate below the Nyquist frequency. However, there is a unique bandlimited signal that samples to , which is given by the Whittaker-Shannon interpolation of , at rate as no aliasing occurs above the Nyquist frequency. Unfortunately, sufficiently high sampling rates cannot always be produced. Aliasing is detrimental to many signal processing applications, so in order to process continuous time signals using discrete time tools, it is often necessary to find ways to avoid it other than increasing the sampling rate. Thus, anti-aliasing filters, are of practical importance.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?