| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module is one in a collection of modules designed for teaching INEW 2338 Advanced Java (Web) at Austin Community College in Austin, TX.
I recommend that you open another copy of this module in a separate browser window and use the following links to easily find and view the Figures and Listings while you are reading about them.
Servlets are modules that run inside request/response-oriented servers, such as Java-enabled web servers, and extend them in some manner. For example, a servlet might be responsible for taking data in an HTML order-entry form and applying the business logic used to update a company's order database.
Servlets are to servers what applets are to browsers. The Servlet API, which you use to write servlets, assumes nothing about how a servlet is loaded, the server environment in which the servlet runs, or the protocol used to transmit data to and from the user. This allows servlets to be embedded in many different web servers.
Servlets are an effective substitute for CGI scripts. They provide a way to generate dynamic documents that is both easier to write and faster to run. They also address the problem of doing server-side programming with platform-specific APIs.
In some ways, a servlet is similar to an applet. An applet is a chunk of Java code that executes under control of a browser. A servlet is a chunk of Java code that executes under control of a server program.
You must run your servlet under the control of a Java-enabled server program. The first few modules in this sub-collection will use the Apache Tomcat server for that purpose.
Please note that the use of servlets is not restricted to HTTP servers. However, the discussion in this lesson and most of the follow-on modules will generally apply only to HTTP servers.
In this module, I will discuss servlets using a sample servlet program named Servlet01.java as a guide. A complete listing of the program is shown in Listing 6 .
This program will illustrate some, but not all of material that I will discuss in this module. The purpose of this program is to illustrate a very simple servlet and to serve as a vehicle for discussion ofvarious aspects of servlets.
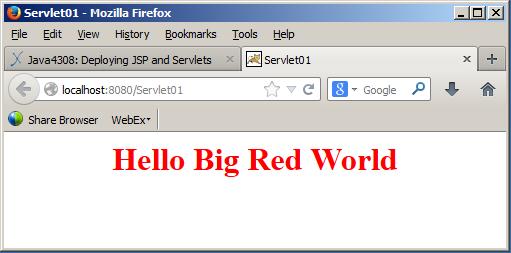
The servlet produces the screen output in the browser shown in Figure 1 .
Figure 1 - Output from Servlet01.java.
Import directives

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Object-oriented programming (oop) with java' conversation and receive update notifications?