| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
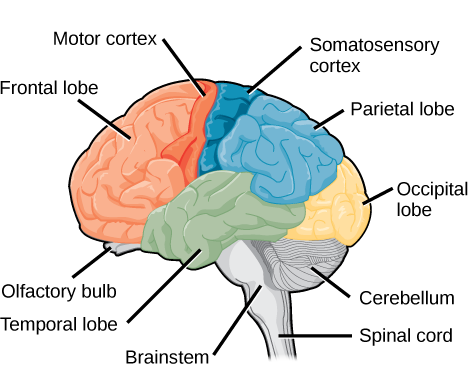
The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain, over the eyes. This lobe contains the olfactory bulb, which processes odors. The frontal lobe also contains the motor cortex, which is important for planning and implementing movement. Areas within the motor cortex map to different muscle groups, and there is some organization to this map, as shown in [link] . For example, the neurons that control movement of the fingers are next to the neurons that control movement of the hand. Neurons in the frontal lobe also control cognitive functions like maintaining attention, speech, and decision-making. Studies of humans who have damaged their frontal lobes show that parts of this area are involved in personality, socialization, and assessing risk.
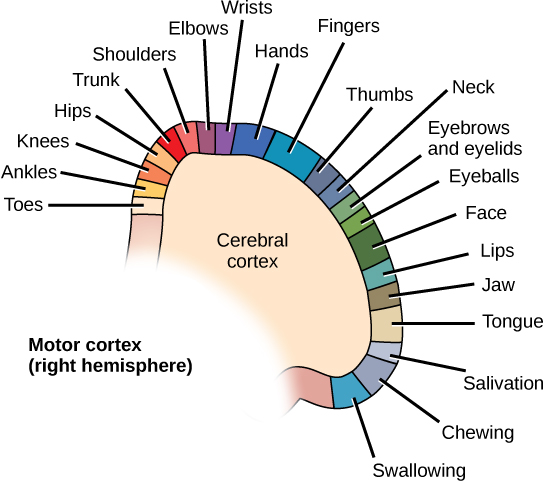
The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain. Neurons in the parietal lobe are involved in speech and also reading. Two of the parietal lobe’s main functions are processing somatosensation—touch sensations like pressure, pain, heat, cold—and processing proprioception—the sense of how parts of the body are oriented in space. The parietal lobe contains a somatosensory map of the body similar to the motor cortex.
The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain. It is primarily involved in vision—seeing, recognizing, and identifying the visual world.
The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by your ears and is primarily involved in processing and interpreting sounds. It also contains the hippocampus (Greek for “seahorse”)—a structure that processes memory formation. The hippocampus is illustrated in [link] . The role of the hippocampus in memory was partially determined by studying one famous epileptic patient, HM, who had both sides of his hippocampus removed in an attempt to cure his epilepsy. His seizures went away, but he could no longer form new memories (although he could remember some facts from before his surgery and could learn new motor tasks).
One small but critically important part of the brain is the hypothalamus, shown in [link] . The hypothalamus controls the endocrine system by sending signals to the pituitary gland, a pea-sized endocrine gland that releases several different hormones that affect other glands as well as other cells. This relationship means that the hypothalamus regulates many important behaviors that are controlled by these hormones. The hypothalamus is the body’s thermostat—it makes sure key functions like food and water intake, energy expenditure, and body temperature are kept at appropriate levels. Neurons within the hypothalamus also regulate circadian rhythms, sometimes called sleep cycles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?