| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The already familiar direction of heat transfer from hot to cold is the basis of our first version of the second law of thermodynamics .
Heat transfer occurs spontaneously from higher- to lower-temperature bodies but never spontaneously in the reverse direction.
Another way of stating this: It is impossible for any process to have as its sole result heat transfer from a cooler to a hotter object.
Now let us consider a device that uses heat transfer to do work. As noted in the previous section, such a device is called a heat engine, and one is shown schematically in [link] (b). Gasoline and diesel engines, jet engines, and steam turbines are all heat engines that do work by using part of the heat transfer from some source. Heat transfer from the hot object (or hot reservoir) is denoted as , while heat transfer into the cold object (or cold reservoir) is , and the work done by the engine is . The temperatures of the hot and cold reservoirs are and , respectively.
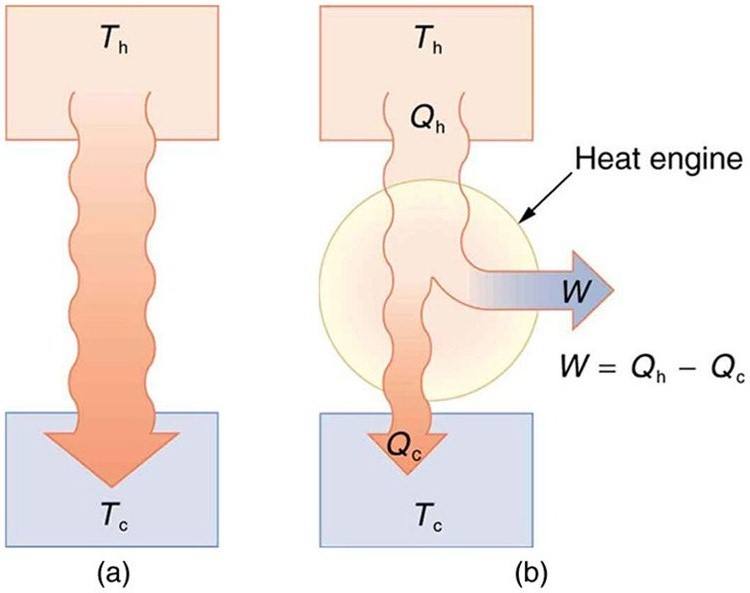
Because the hot reservoir is heated externally, which is energy intensive, it is important that the work is done as efficiently as possible. In fact, we would like to equal , and for there to be no heat transfer to the environment ( ). Unfortunately, this is impossible. The second law of thermodynamics also states, with regard to using heat transfer to do work (the second expression of the second law):
It is impossible in any system for heat transfer from a reservoir to completely convert to work in a cyclical process in which the system returns to its initial state.
A cyclical process brings a system, such as the gas in a cylinder, back to its original state at the end of every cycle. Most heat engines, such as reciprocating piston engines and rotating turbines, use cyclical processes. The second law, just stated in its second form, clearly states that such engines cannot have perfect conversion of heat transfer into work done. Before going into the underlying reasons for the limits on converting heat transfer into work, we need to explore the relationships among , , and , and to define the efficiency of a cyclical heat engine. As noted, a cyclical process brings the system back to its original condition at the end of every cycle. Such a system's internal energy is the same at the beginning and end of every cycle—that is, . The first law of thermodynamics states that
where is the net heat transfer during the cycle ( ) and is the net work done by the system. Since for a complete cycle, we have

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?