| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So: -(-128) = -128.
Because 128 is out of the range of signed 8bits numbers.
Addition and Subtraction is done using following steps:

The multiplying is done using following steps:


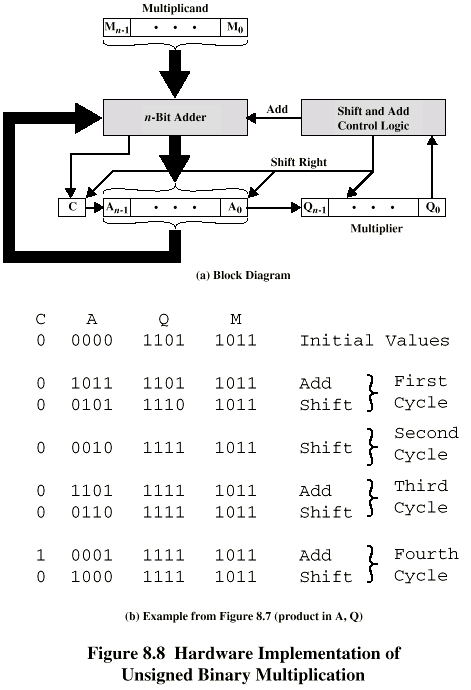


Example of Booth’s Algorithm:

We can represent a real number in the form
This number can be stored in a binary word with three fields:
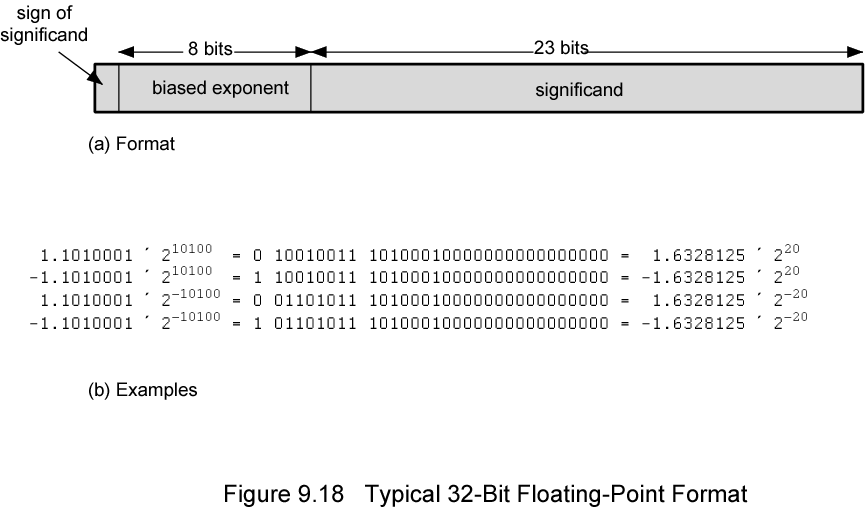
(A fixed value, called the bias, is subtracted from the biased exponent field to get the true exponent value (E). Typically, the bias equal , where k is the number of bits in the binary exponent)
The most important floating-point representation is defined in IEEE Standard 754 [EEE8]. This standard was developed to facilitate the portability of programs from one processor to another and to encourage the development of sophisticated, numerically oriented programs. The standard has been widely adopted and is used on virtually all contemporary processors and arithmetic coprocessors.
The IEEE standard defines both a 32-bit (Single-precision) and a 64-bit (Double-precision) double format with 8-bit and 11-bit exponents, respectively. Binary floating-point numbers are stored in a form where the MSB is the sign bit, exponent is the biased exponent, and "fraction" is the significand. The implied base (B) is 2.
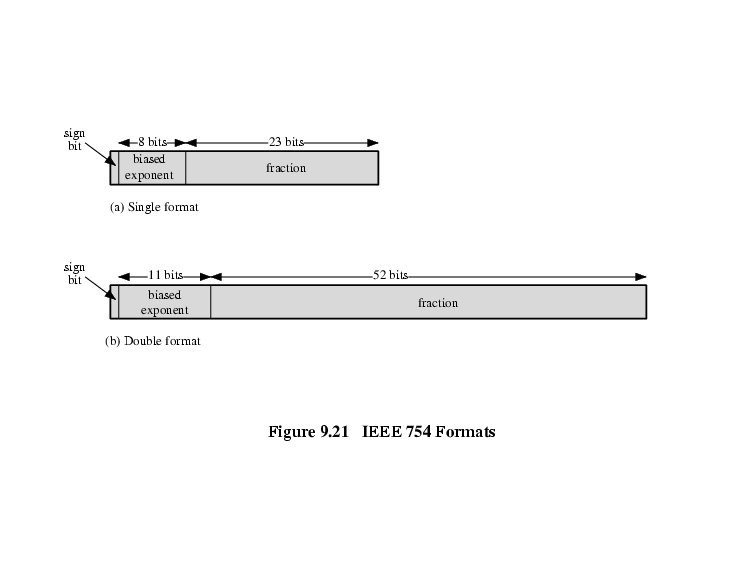
Not all bit patterns in the IEEE formats are interpreted in die usual way; instead, some bit patterns are used to represent special values. Three special cases arise:
This can be summarized as:

Single-precision 32 bit
A single-precision binary floating-point number is stored in 32 bits.
The number has value v:
v = s × × m
Where
s = +1 (positive numbers) when the sign bit is 0
s = −1 (negative numbers) when the sign bit is 1
e = Exp − 127 (in other words the exponent is stored with 127 added to it, also called "biased with 127")
m = 1.fraction in binary (that is, the significand is the binary number 1 followed by the radix point followed by the binary bits of the fraction). Therefore, 1 ≤ m<2.
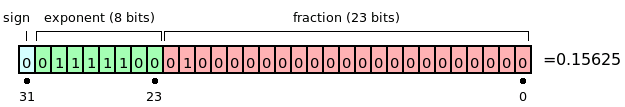
In the example shown above:
S=1
E= 011111100(2) -127 = -3
M=1.01 (in binary, which is 1.25 in decimal).
The represented number is: +1.25 × 2−3 = +0.15625.
The basic operations for floating-point and
For addition and subtraction, it is necessary lo ensure that both operands have the same exponent value. I his may require shifting the radix point on one of the operands to achieve alignment. Multiplication and division are more straightforward.
A floating-point operation may produce one of these conditions:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?