| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ASKING QUESTIONS
A. Form groups with four members in each. Look around in the classroom and take turns to ask questions. Use the new vocabulary that you have learned to help you find the missing objects.
Start each question as follows:
| Some words to help you answer: | under | In front of | on | behind | on top of | next to |
C. Now, write down the six questions that you asked the group with their answers.
i) ………………………………………………………………………………….
ii) ………………………………………………………………………………….
iii) ………………………………………………………………………………….
iv) ………………………………………………………………………………….
v) ………………………………………………………………………………….
vi) ………………………………………………………………………………….
vii) ………………………………………………………………………………….
viii) ………………………………………………………………………………….
ix) ………………………………………………………………………………….
x) ………………………………………………………………………………….
xi) ………………………………………………………………………………….
xii) ………………………………………………………………………………….
D. Change the following sentences into questions. Remember that we put a question mark at the end of a question sentence. (?)
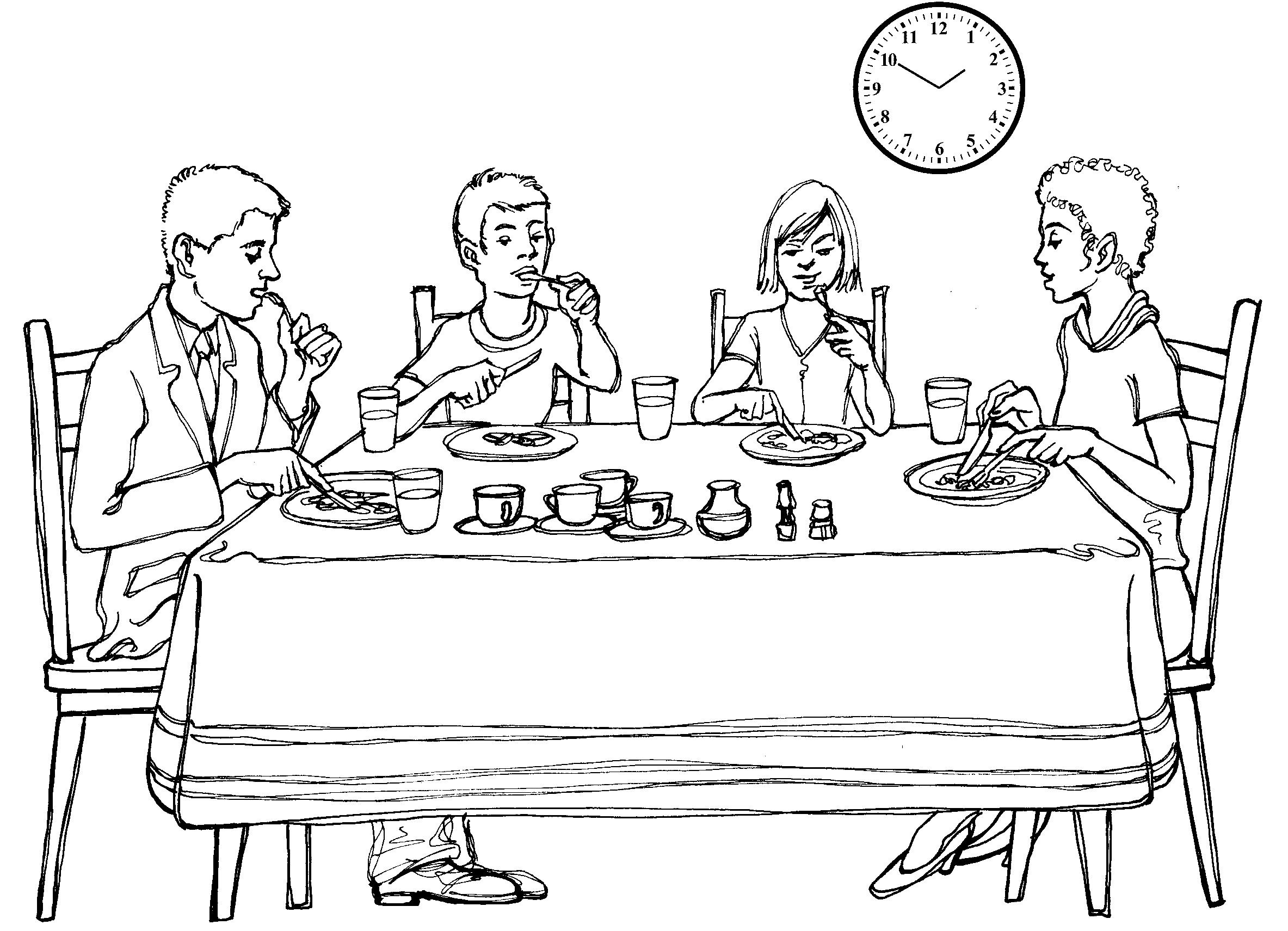
Example : They are having lunch. Are they having lunch?
a) There are four plates on the table.
……………………………………………………………………………….
b) They are drinking milk.
………………………………………………………………………………
c) There is a tablecloth over the table.
………………………………………………………………………………
d) There is a vase with flowers on the table.
……………………………………………………………………………..
e) They are eating with knives and forks.
…………………………………………………………………………….
Can you say when we use “is” and when we use “are”? Use the previous sentences to help you decide.
Look at the picture and say whether the statements about the picture are true (T), false (F) or not supported by enough evidence (NEE).
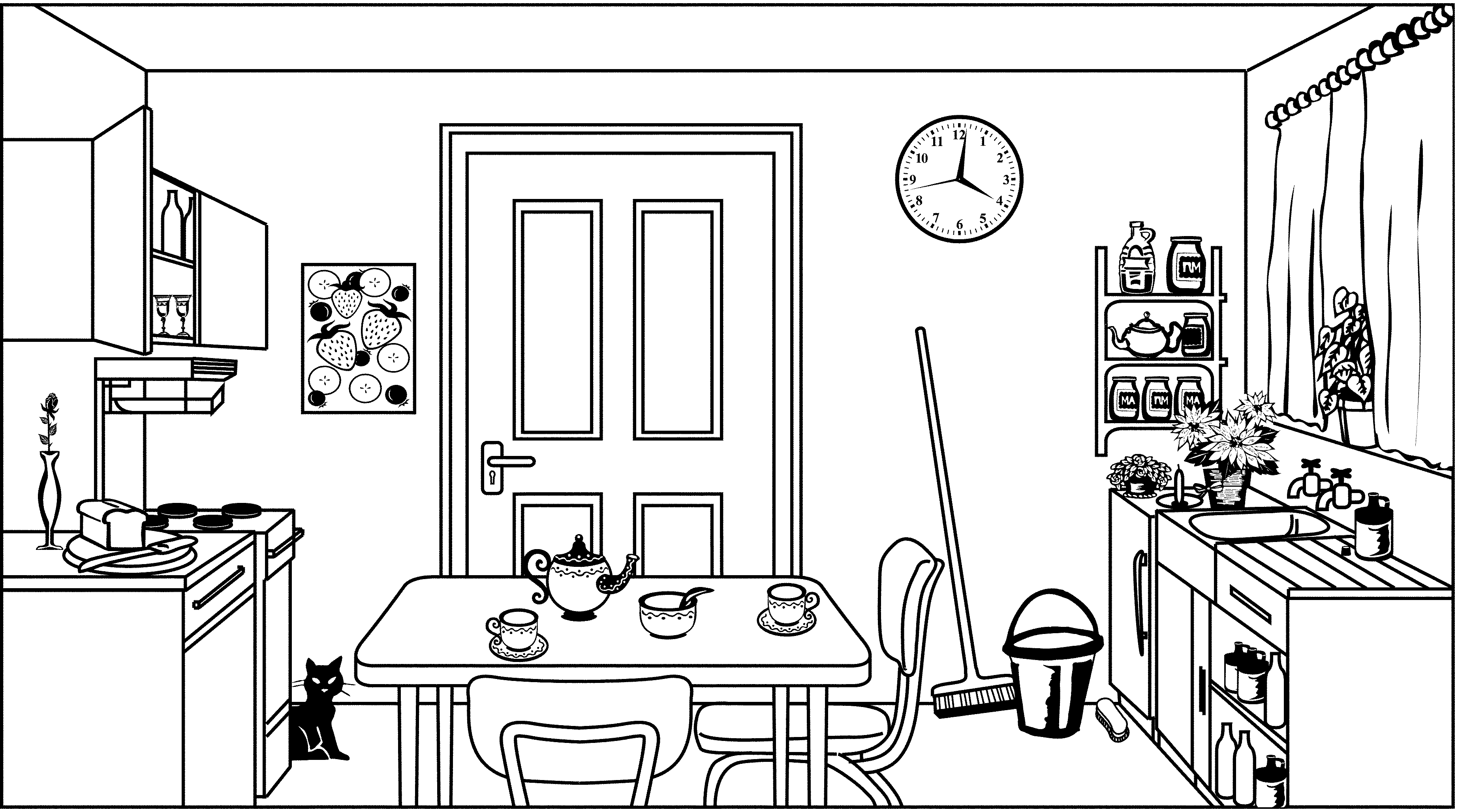
| STATEMENTS | TRUE | FALSE | NEE |
| a) There are three cups on the table. | |||
| b) The knife is between the vase and the loaf of bread. | |||
| c) There are two glasses in the cupboard. | |||
| d) There are three potplants. | |||
| e) The cat is lying behind the stove. | |||
| f) The kitchen door has a broken lock. | |||
| g) The bucket is full of soapy water. | |||
| h) The candle is standing on top of the refrigerator. | |||
| i) There are curtains in front of the windows. | |||
| j) There is a teapot on the shelf against the wall. | |||
| k) It is late afternoon. | |||
| l) The cupboard is open. |
First choose a picture. Then choose a word that matches your picture from the list below. Decide in which room you will do what your word says. Choose one of these rooms: kitchen , lounge , bedroom , bathroom . Then write your sentence
For example : I play table tennis in the playroom.
REMEMBER:
If it is one person ( but not ‘I’ or ‘you’) that is doing something you must add - s or - es to the word that you choose!
I He
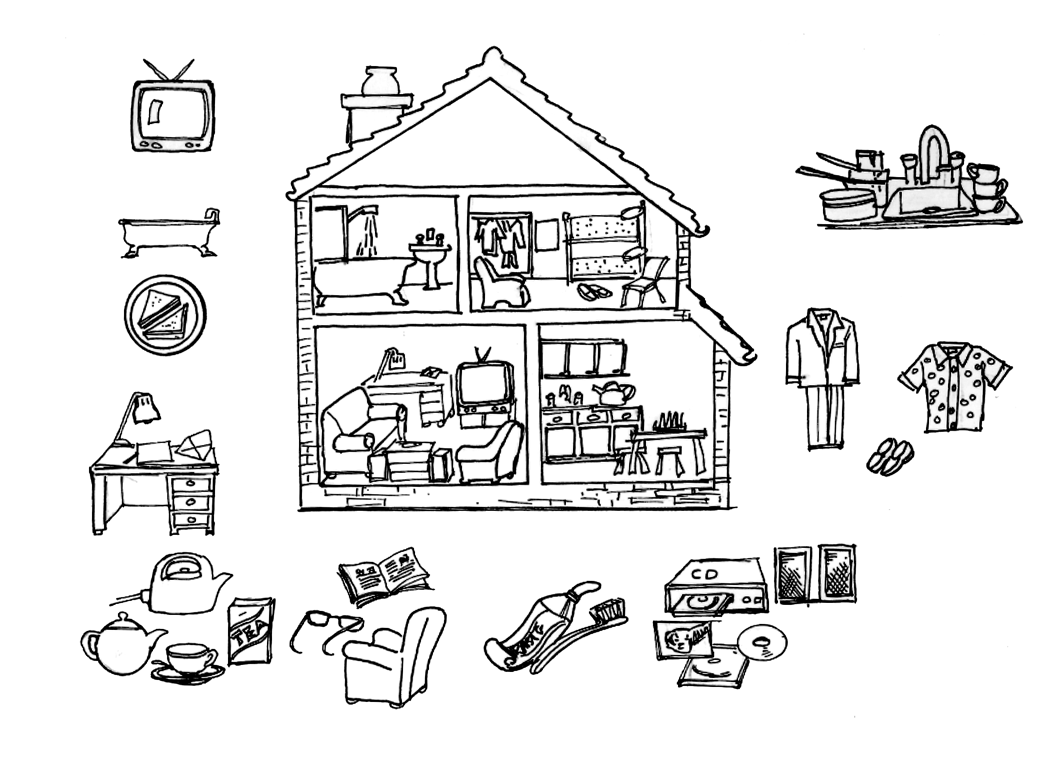
She
They.........
We
She
We He They I
SOME MORE HELP
lunch; letters; book; teeth; music; tea; clothes; table tennis; dishes; television
watch make bath eat listen to write play brush put on wash read
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………….
The learner will be able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
We know this when the learner:
4.5 uses developing knowledge of language structure:
4.5.3 begins to use a wider range of punctuation (e.g. apostrophes).
The learner will able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
We know this when the learner:
5.4 transfers information from one mode to another (e.g. chart to text):
5.4.3 uses information from a chart, graph or diagram to write a short text.
The learner will know and be able to use the sounds, words and grammar of the language and interpret texts.
We know this when the learner:
6.1 understands and uses some question forms, such as ‘Why didn’t ...?’, ‘Have you ever ...?’, ‘Do you think ...?’
6.2 uses the tenses introduced in the Foundation Phase to communicate orally and in writing, e.g.:
6.2.1 simple present tense.
Activity 1
a) Are there four plates on the table?
b) Are they drinking milk?
c) Is there a cloth over the table?
d) Is there a vase with flowers on the table?
e) Are they eating with knives and forks?
We use is when we are talking of one person or object and are when we are talking about more than one person or object.
Activity 2
| STATEMENTS | TRUE | FALSE | NEE |
| a) There are three cups on the table. | X | ||
| b) The knife is between the vase and the loaf of bread. | X | ||
| c) There are two glasses in the cupboard. | X | ||
| d) There are three potplants. | X | ||
| e) The cat is lying behind the stove. | X | ||
| f) The kitchen door has a broken lock. | X | ||
| g) The bucket is full of soapy water. | X | ||
| h) The candle is standing on top of the refrigerator. | X | ||
| i) There are curtains in front of the windows. | X | ||
| j) There is a teapot on the shelf against the wall. | X | ||
| k) It is late afternoon. | X | ||
| l) The cupboard is open. | X |
Activity 3
a) I watch television in the lounge.
b) She baths in the bathroom.
c) We eat lunch in the kitchen.
d) She writes letters in the lounge.
e) We make tea in the kitchen.
f) He reads a book in the lounge.
g) They brush their teeth in the bathroom.
h) I listen to music in the lounge.
i) They put on clothes in the bedroom.
j) He washes the dishes in the kitchen.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?