| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Geometry
1. Let us revise the work that you did in Grade 4. At the same time you can see how good your memory is! For the following activity you will have to use your father’s hammer and nails. Just keep your thumb out of the way!
Place the nails about 1,5 cm apart.
DO YOU STILL REMEMBER?
A quadrilateral is any figure with 4 sides and 4 angles.
A square has four sides of equal length and four 90º angles.
The opposite sides of a rectangle are of equal length and all four angles are 90º.
A triangle is any figure with 3 angles and 3 sides.
1.1 Form the following figures with rubber bands on the nail board.
1.2 Draw two of each figure on the dotted sheet (p. 5).
Quadrilateral
Square
Rectangle
Triangle
1.3 Have a class discussion: Make a list of all the similarities between your figures on the peg-board.
1.4 Now draw and examine the figures on your dotted page (page 4) and, as a class, see how much dissimilarity you can find among them.
1. Page through old newspapers and magazines and cut out examples of quadrangles, squares, rectangles and triangles. Paste them into the appropriate boxes below. Get a friend to check whether you have done it correctly. (Hint: See whether the qualities of the figure match those of the example that your friend pasted in.)
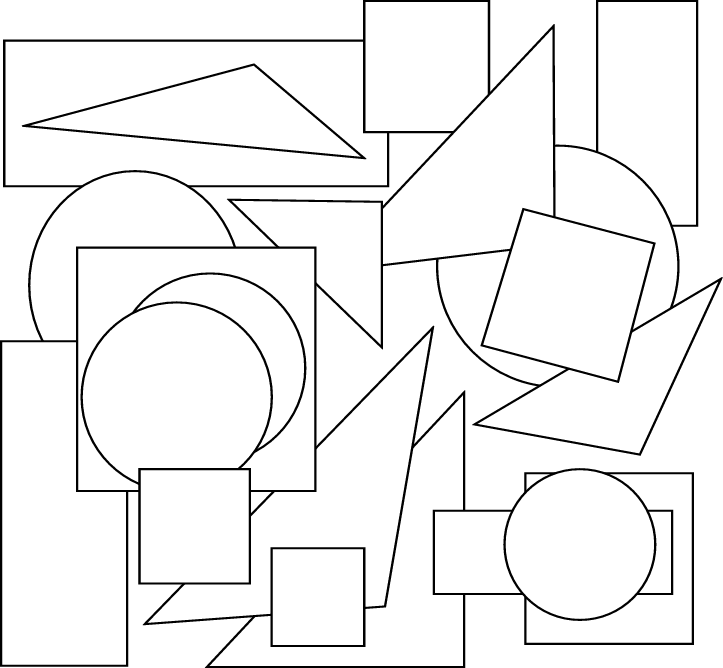
1. Colour the parts of all the triangles you can see in purpleHow many triangles are there?
2. Colour all the circles in pink. How many circles are there?
3. Colour all the squares in red. How many squares are there?
4. Colour all the rectangles in green. How many rectangles are there?
Although it sounds very simple, it is still extremely important for you to know how many sides and angles a figure has, because it can help us to classify polygons without much trouble. Use the drawings below and then complete the table that follows.

A triangle, quadrilateral and a pentagon

A hexagon, heptagon and an octagon
| Number of sides in the polygon | 3 | 4 | 5 | ......... | ......... | 8 | 12 | 100 | 220 |
| Number of triangles in the polygon | 1 | ......... | ......... | 4 | 5 | ......... | ......... | ......... | ......... |
This activity is an assignment for your portfolio. Read the instructions as well as the assessment criteria carefully before you start. Ask your teacher to explain where necessary.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?