| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Vector fields are an important tool for describing many physical concepts, such as gravitation and electromagnetism, which affect the behavior of objects over a large region of a plane or of space. They are also useful for dealing with large-scale behavior such as atmospheric storms or deep-sea ocean currents. In this section, we examine the basic definitions and graphs of vector fields so we can study them in more detail in the rest of this chapter.
How can we model the gravitational force exerted by multiple astronomical objects? How can we model the velocity of water particles on the surface of a river? [link] gives visual representations of such phenomena.
[link] (a) shows a gravitational field exerted by two astronomical objects, such as a star and a planet or a planet and a moon. At any point in the figure, the vector associated with a point gives the net gravitational force exerted by the two objects on an object of unit mass. The vectors of largest magnitude in the figure are the vectors closest to the larger object. The larger object has greater mass, so it exerts a gravitational force of greater magnitude than the smaller object.
[link] (b) shows the velocity of a river at points on its surface. The vector associated with a given point on the river’s surface gives the velocity of the water at that point. Since the vectors to the left of the figure are small in magnitude, the water is flowing slowly on that part of the surface. As the water moves from left to right, it encounters some rapids around a rock. The speed of the water increases, and a whirlpool occurs in part of the rapids.
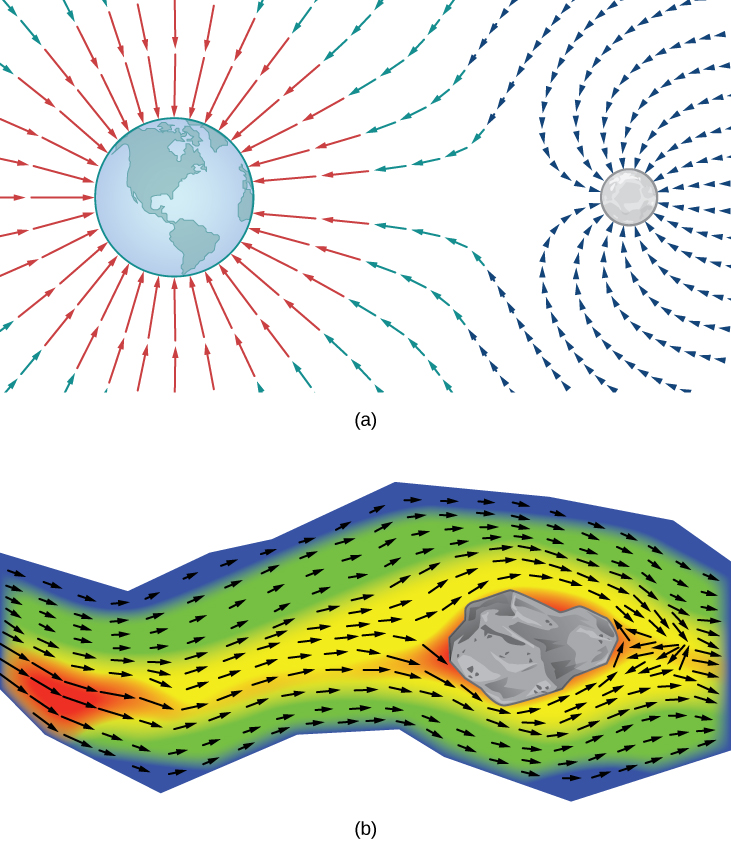
Each figure illustrates an example of a vector field. Intuitively, a vector field is a map of vectors. In this section, we study vector fields in and
A vector field in is an assignment of a two-dimensional vector to each point of a subset D of The subset D is the domain of the vector field.
A vector field F in is an assignment of a three-dimensional vector to each point of a subset D of The subset D is the domain of the vector field.
A vector field in can be represented in either of two equivalent ways. The first way is to use a vector with components that are two-variable functions:
The second way is to use the standard unit vectors:
A vector field is said to be continuous if its component functions are continuous.
Let be a vector field in Note that this is an example of a continuous vector field since both component functions are continuous. What vector is associated with point
Substitute the point values for x and y :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?