| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By now, we are familiar with writing equations that describe a line in two dimensions. To write an equation for a line, we must know two points on the line, or we must know the direction of the line and at least one point through which the line passes. In two dimensions, we use the concept of slope to describe the orientation, or direction, of a line. In three dimensions, we describe the direction of a line using a vector parallel to the line. In this section, we examine how to use equations to describe lines and planes in space.
Let’s first explore what it means for two vectors to be parallel. Recall that parallel vectors must have the same or opposite directions. If two nonzero vectors, and are parallel, we claim there must be a scalar, such that If and have the same direction, simply choose If and have opposite directions, choose Note that the converse holds as well. If for some scalar then either and have the same direction or opposite directions so and are parallel. Therefore, two nonzero vectors and are parallel if and only if for some scalar By convention, the zero vector is considered to be parallel to all vectors.
As in two dimensions, we can describe a line in space using a point on the line and the direction of the line, or a parallel vector, which we call the direction vector ( [link] ). Let be a line in space passing through point Let be a vector parallel to Then, for any point on line we know that is parallel to Thus, as we just discussed, there is a scalar, such that which gives
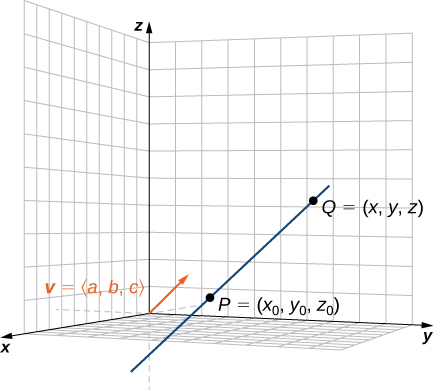
Using vector operations, we can rewrite [link] as
Setting and we now have the vector equation of a line :
Equating components, [link] shows that the following equations are simultaneously true: and If we solve each of these equations for the component variables we get a set of equations in which each variable is defined in terms of the parameter t and that, together, describe the line. This set of three equations forms a set of parametric equations of a line :
If we solve each of the equations for assuming are nonzero, we get a different description of the same line:
Because each expression equals t , they all have the same value. We can set them equal to each other to create symmetric equations of a line :
We summarize the results in the following theorem.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?