| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You have just read about two pathways in glucose catabolism—glycolysis and the citric acid cycle—that generate ATP. Most of the ATP generated during the aerobic catabolism of glucose, however, is not generated directly from these pathways. Rather, it is derived from a process that begins with moving electrons through a series of electron transporters that undergo redox reactions. This causes hydrogen ions to accumulate within the matrix space. Therefore, a concentration gradient forms in which hydrogen ions diffuse out of the matrix space by passing through ATP synthase. The current of hydrogen ions powers the catalytic action of ATP synthase, which phosphorylates ADP, producing ATP.
The electron transport chain ( [link] ) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of glucose metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants; in animals, it enters the body through the respiratory system. Electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resemble a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where the electrons reduce molecular oxygen, producing water. There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled I through IV in [link] , and the aggregation of these four complexes, together with associated mobile, accessory electron carriers, is called the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes.
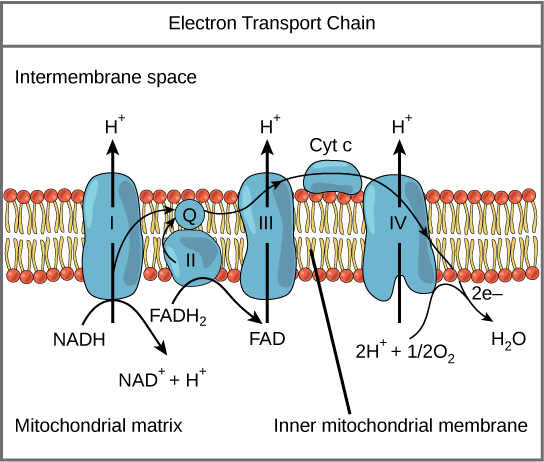
To start, two electrons are carried to the first complex aboard NADH. This complex, labeled I, is composed of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and an iron-sulfur (Fe-S)-containing protein. FMN, which is derived from vitamin B 2, also called riboflavin, is one of several prosthetic groups or co-factors in the electron transport chain. A prosthetic group is a non-protein molecule required for the activity of a protein. Prosthetic groups are organic or inorganic, non-peptide molecules bound to a protein that facilitate its function; prosthetic groups include co-enzymes, which are the prosthetic groups of enzymes. The enzyme in complex I is NADH dehydrogenase and is a very large protein, containing 45 amino acid chains. Complex I can pump four hydrogen ions across the membrane from the matrix into the intermembrane space, and it is in this way that the hydrogen ion gradient is established and maintained between the two compartments separated by the inner mitochondrial membrane.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?