| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 3 learners continue to expand their vocabulary by listening and reading a variety of texts such as poem, stories, riddles and doing word puzzles.
These modules consolidate and revise the vocabulary and phonics introduced in Grade 2. More opportunities are given for written work producing longer texts of more varied kinds. Learners should not be afraid to make mistakes as the building of confidence and fluency should take priority above perfect written work.
Time scheduled for the modules
All learners should work through all eight modules as the phonics and spelling requirements are spread over these modules. The educator should however allow learners to complete them at their own pace namely ± two modules per term.
New words are introduced and learnt before learners read the story of Thomas. Thomas leaves his home and friends to follow the advice of strangers. This leads to his death. The life cycle of frogs is studied in this module.
Learners are exposed to a mindmap of creatures in the forest.
Integration of themes.
Learners should heed the warnings of friends and parents and be careful of strangers.
Keep ponds, rivers clean because of the creatures that inhabit them.
By studying the life cycle of the frog learners become aware of the wonder of nature and their responsibility towards it.
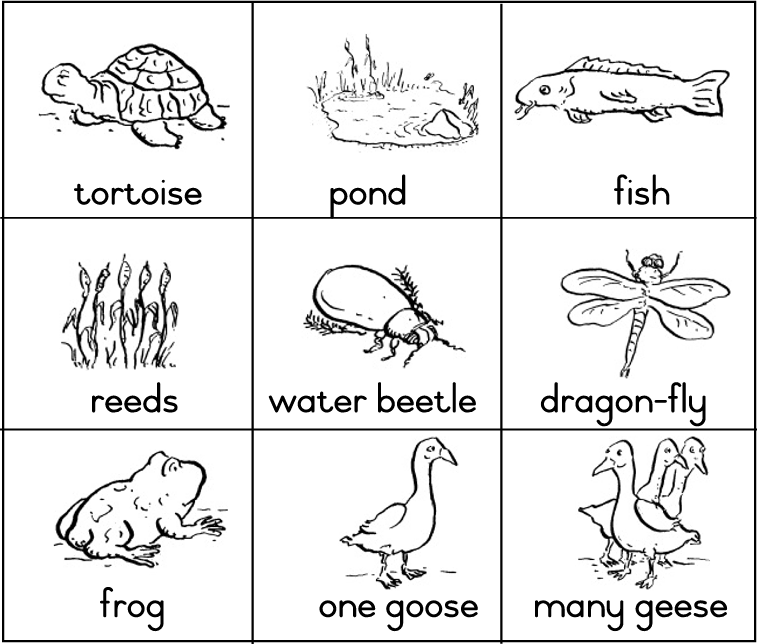
Once upon a time there lived a tortoise called Thomas.
He lived in a land far, far away.
He lived near a pond.
He had many friends to talk to.
| LO 2.1 | LO 2.5 | LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.8.1 |
Thomas liked to tell the fish in the pond what he had seen in the forest.
He liked to tell the dragonfly how beautiful she was.
He liked to tell the frog where he could find big fat flies for his dinner.
He liked to tell the water beetle how to float on his back.
He liked to talk to all his friends.
He talked the whole day long.
He talked and talked and never stopped.
| LO 3.2.2 | LO 3.5 | LO 4.12 |
1. He liked to tell the fish in the pond …………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. He liked to tell the dragonfly …………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
3. He liked to tell the frog ………………………………………………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
4. He liked to tell the water beetle ………………………………………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
5. He talked and talked and ……………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 4.3 | LO 4.12 |

| LO 1.3 | LO 2.5 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner will be able to listen for information and enjoyment, and respond appropriately and critically in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner shows understanding of descriptions by noting relevant information:
1.1.2 predicts what the story will be about from the title;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner answers questions using words and phrases;
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner talks about a picture, photograph or object:
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner begins to make meaning of written text by reading with the teacher:
3.2.2 predicts what a book is about from the title;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner recognises and makes meaning of letters and words:
3.3.1 recognises on sight an increasing number of high-frequency words;
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner reads aloud using correct pronunciation and appropriate stress:
Assessment Standard 3.8: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
3.8.1 reads and follows instructions (e.g. how to play a game).
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner will be able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes individual words such as labels:
Assessment Standard 4.3: We know this when the learner spells common words correctly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?