| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
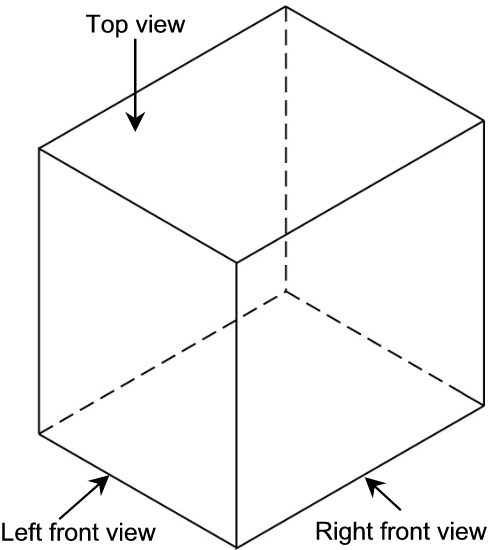
Underline:
Colour the views in the following way: Front: Blue
Side: Green
Top: Red


Background:
Before we try individually to draw a three-dimensional object, we are going to compare shapes of planes in a drawing with shapes of the real object.

Drawing A and B
| Number of plane | Type of face on sketch | Shape on real object |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 |
Something interesting:
If we suppose that these are sketches of the same shed, try to explain why.
Background:
A three-dimensional shape such as a cube also has vertical and horizontal planes.
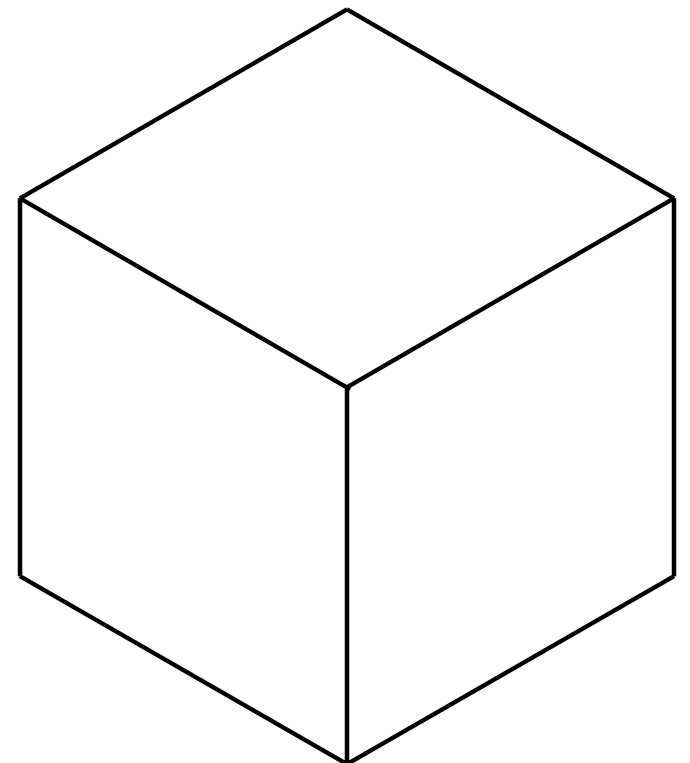
Circle:
A cube has 2/ 4/ 6 horizontal and 2/ 4/ 6 vertical planes.
[LO 1.3]
ASSIGNMENT 4A:
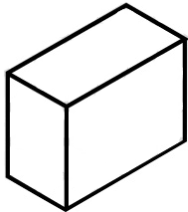
a) How many horizontal planes does a wooden block have that stands like
this?
And vertical planes?

b) How many horizontal planes does a wooden block have that stands like
this?
And vertical planes?
c) What conclusion can you draw from this? Complete:
A wooden block/rectangular shape always has horizontal and
vertical planes.

a) Redraw the three visible planes on carbon paper (numbers 4, 5 and 6 above).
b) Cut out the three planes.
c) Use three pieces of different coloured cardboard and cut out two examples of each plane from the colours (six parts with two of each colour) (two of number 6, two of number 5, two of number 4).
d) Build the box on the grid (annexure 1) by gluing the parts as shown in the sequence that was indicated above. Use Prestik to stick the parts onto the grid.
e) Now draw the box in pencil on the grid. First draw the visible lines and then the invisible lines in dotted lines.
A Challenge:
f) Suppose that plane 4 is a flap that can open. Close flap 4. Now draw the box in pencil with its open flap on the grid. First draw all the visible lines and then the invisible lines.
Learning Outcomes(LOs)
LO 1
TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SKILLS
The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technologies
Assessment Standards(ASs)
We know this when the learner:
1.3 performs, where appropriate, scientific investigations about concepts relevant to a problem, need or opportunity using science process skills.
Assignment 1
Learners could do it individually after a learning discussion by the teacher.
Assignment 2A
The teacher could do one together with the learners in order to explain it to them, and the learners could then do the rest individually. Make a transparency of the page and use coloured transparency pens.
Assignment 2B
The teacher explains, using a cigarette box or matchbox. The different positions are then indicated in a practical way before the learners draw it. For instance, B could be done with the learners, and then they could be told to do C and D by themselves.
Assignment 3
Let groups of learners, for instance, do drawing A. They should then check and the reasons for the answers. Then learners should do drawing B individually, after which it could be checked. Have a class discussion about the relevant questions.
Assignment 4A
Discuss the questions by illustrating practically with a wooden block and let learners fill in the answers.
Assignment 4B
This is a practical exercise. Each learner should therefore have scissors, Prestik, a 30 60 grid (Addendum 1) and three pieces of coloured cardboard to complete the assignment. Do the assignment together with the learners.
Assignment 5
Each learner can evaluate his/her progress individually. Emphasise the fact that each learner should be honest, as the teacher would be able to see from the practical work whether the learner was honest or not.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?