| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Polar substances present problems for the membrane. While some polar molecules connect easily with the outside of a cell, they cannot readily pass through the lipid core of the plasma membrane. Additionally, while small ions could easily slip through the spaces in the mosaic of the membrane, their charge prevents them from doing so. Ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride must have special means of penetrating plasma membranes. Simple sugars and amino acids also need help with transport across plasma membranes, achieved by various transmembrane proteins (channels).
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across a space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of ammonia in a room filled with people. The ammonia gas is at its highest concentration in the bottle; its lowest concentration is at the edges of the room. The ammonia vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the ammonia as it spreads. Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion ( [link] ). Diffusion expends no energy. On the contrary, concentration gradients are a form of potential energy, dissipated as the gradient is eliminated.
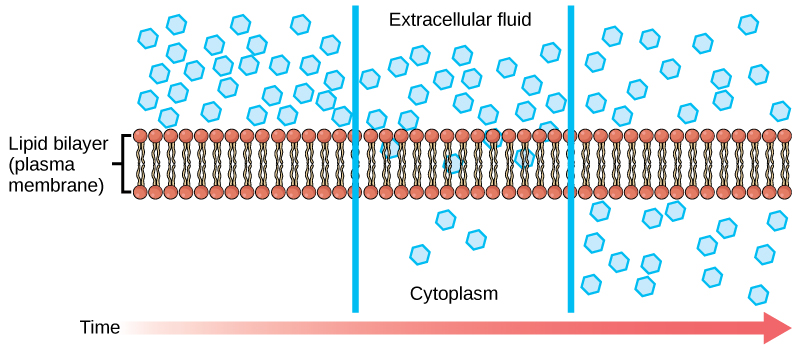
Each separate substance in a medium, such as the extracellular fluid, has its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other materials. In addition, each substance will diffuse according to that gradient. Within a system, there will be different rates of diffusion of the different substances in the medium.
Molecules move constantly in a random manner, at a rate that depends on their mass, their environment, and the amount of thermal energy they possess, which in turn is a function of temperature. This movement accounts for the diffusion of molecules through whatever medium in which they are localized. A substance will tend to move into any space available to it until it is evenly distributed throughout it. After a substance has diffused completely through a space, removing its concentration gradient, molecules will still move around in the space, but there will be no net movement of the number of molecules from one area to another. This lack of a concentration gradient in which there is no net movement of a substance is known as dynamic equilibrium. While diffusion will go forward in the presence of a concentration gradient of a substance, several factors affect the rate of diffusion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ap biology - part 1: the cell' conversation and receive update notifications?