| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The way in which schools operate is something that has undergone much research recently, especially since the advent of modeling technologies that can accurately represent fish populations. The basics of the mechanisms of schooling are known, but much is yet to be understood. It has been determined that across most species, the mechanisms of schooling are more or less conserved and rely on individual physiology and environment (Gobert et al 2001). Mechanisms are evolutionarily relevant to the study of aggregation because they demonstrate the results of generations of selective pressure, and the mechanism behind how the school physically operates is the basis for why predator avoidance, foraging, and sexual schooling can occur.
Sensory perception, or some form of identifying how one relates to others spatially within a school, is imperative to avoid collisions and synchronize movement. Models show that for the school to move and change direction, strong boundaries of repulsion, neutrality, and attraction must exist in order to shape the school. This suggests a sensory mechanism works to establish these regions and provide for the uniformity within schools. (Grunbam et al 2007) . This is supported by response mechanisms at the individual level that create these accommodations (Gueron 1996). It is unknown when these mechanisms evolved, however it is surmised that they evolved in conjunction with the aggregate behavior of schools. Either way, these mechanisms subtly allow competition for safe positions to continue while mostly maintaining a constant dynamic that allows the school to benefit the individuals that comprise it.
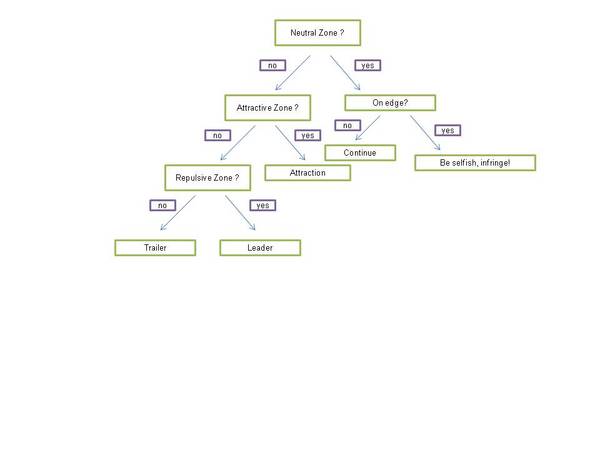
This flow chart shows the mechanism of identifying how one should alter direction in order to stay with the school (Gueron 1996). There are several zones in which evaluation needs to occur. The neutral zone means that you are neither too close nor too far from any one, and if one is on the edge and in the neutral zone, you may try to squeeze into the repulsive zone as it is more advantageous for you to be closer to the school. Even in the mechanics of schooling, the individual selfishness that is at the heart of schooling is very evident. If one is not on the edge, then one will try to maintain your position far enough from each fish so that you are out of your neighbors’ repulsive zones, but not so far so that you are in the attractive zones. The repulsive zone means one is too close, and the attractive zone means one is too far. These zones are models of how position evaluation likely occurs in order to maintain the equal spacing and uniformity of the school (Grunbam et al 2007).
The density and volume of a school often dictate the schools shape and mechanics. It is observed that under specific positions and velocities, aggregations are more likely to form. However, it is not known whether these positions and velocities occur by chance or if they are contrived by individuals seeking to school (Cucker and Mordecki 2007). Once schools are made, the size of the school is regulated by normal distributions, and fission or fusion events occur when the school is either too large or too small in relation to normal distribution (Niwa 1998). In order for these events to occur, an optimal degree of synchronization must occur, though it cannot be determined if this synchronization is a function of school size or if individuals adjust synchronization in anticipation of changes (Skaret and Vabo 2008). Additional observations indicate that speed regulates the density of a school, with faster swimming resulting in denser schools (Pitcher 1979). These observations, however, often cannot separate individual intent from coincidental happenings. Studies show that just as predators tailor their hunting styles to suit the school, fishing gear can be evaluated and updated to reflect the hydromechanics within a school (Weihs 1973). The application of this information is a creative way that brings schooling theory and research back to where it initially began - practical ways for humans to acquire food, a noticeable parallel to the coevolution of predator and prey.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mockingbird tales: readings in animal behavior' conversation and receive update notifications?