| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module will begin our study of signals and systems by laying out some of the fundamentals of signal classification. It is essentially an introduction to the important definitions andproperties that are fundamental to the discussion of signals and systems, with a brief discussion of each.
As the names suggest, this classification is determined by whether or not the time axis is discrete (countable) or continuous ( [link] ). A continuous-time signal will contain a value for all real numbers along the time axis.In contrast to this, a discrete-time signal , often created by sampling a continuous signal, willonly have values at equally spaced intervals along the time axis.

The difference between analog and digital is similar to the difference between continuous-time and discrete-time. However, in this casethe difference involves the values of the function. Analog corresponds to a continuous set of possible function values, while digital corresponds to a discreteset of possible function values. An common example of a digital signal is a binary sequence, where the values of the function can only be oneor zero.

Periodic signals repeat with some period , while aperiodic, or nonperiodic, signals do not ( [link] ). We can define a periodic function through the followingmathematical expression, where can be any number and is a positive constant:


Another way of classifying a signal is in terms of its length along its time axis. Is the signal defined for all possible values of time, or for only certain values of time? Mathematically speaking, is a finite-length signal if it is defined only over a finite interval where . Similarly, an infinite-length signal , , is defined for all values:
Causal signals are signals that are zero for all negative time, while anticausal are signals that are zero for all positive time. Noncausal signals are signals that have nonzero values in both positive and negative time ( [link] ).



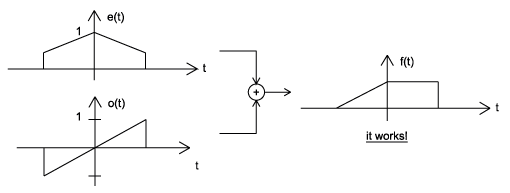
An even signal is any signal such that . Even signals can be easily spotted as they are symmetric around the vertical axis. An odd signal , on the other hand, is a signal such that ( [link] ).

Using the definitions of even and odd signals, we can show that any signal can be written as a combination of an even andodd signal. That is, every signal has an odd-even decomposition. To demonstrate this, we have to look nofurther than a single equation.



A deterministic signal is a signal in which each value of the signal is fixed, being determined by amathematical expression, rule, or table. On the other hand, the values of a random signal are not strictly defined, but are subject to some amount of variability.


Consider the signal defined for all real described by
This signal is continuous time, analog, aperiodic, infinite length, causal, neither even nor odd, and, by definition, deterministic.
This module describes just some of the many ways in which signals can be classified. They can be continuous time or discrete time, analog or digital, periodic or aperiodic, finite or infinite, and deterministic or random. We can also divide them based on their causality and symmetry properties.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?