| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
2. Try doing the following:
1. Constructing a circumscribed circle:
1.7 Conclusion: A . circle can be constructed by
bisecting the of a triangle.
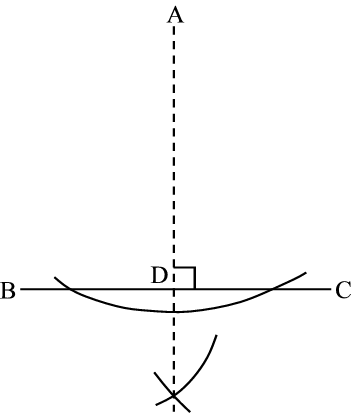
2. Constructing an inscribed circle:
2.7 Conclusion: A circle can be constructed by
bisecting the of a triangle.
1. Required: construct FA ll QR , so that AR = 30 mm.
1.1 Draw an imaginary line (dotted line) FA where the parallel line is required to be.
1.2 Mark A on PR so that AR = 30 mm.
1.3 Position the point of your compasses on R and draw an arc (any size) as indicated.
1.4 Maintaining the setting of your pair of compasses (same size), place the point on A and draw an arc like the previous one.
1.5 Measure the distance, marking it with crosses (x) as indicated.
1.6 Place the compass point on the circle (o) as indicated. This line will intersect the arc and should be on the imaginary line.
1.7 Connect A with the intersecting point of the last drawn line.
1.8 Mark F on PQ. FA will be parallel to QR .
1.9 What does it mean when we say that FA ll QR ?

2. Try doing the following by yourself:
1. You are the owner of a farm in Mpumalanga. You wish to reward one of your farm workers, Michael Mohapi, for his good service of the past 20 years. You present Michael with a stretch of land as a gift. The precondition is that the land must be measured out in the form of a parallelogram according to measurements indicated on a plan.
1.1 The first problem that arises has to do with the fact that Michael does not know what a parallelogram is. Use a sketch to provide Michael with all the characteristics of a parallelogram.
1.2 Also show Michael the mathematical “abbreviation” for a parallelogram, so that he will know what is meant when he sees the relevant "sign".
1.3 Now you have to execute a construction to indicate exactly how the land is to be measured.
| LO 3 |
| Space and Form (geometry)The learner is able to describe and represent features of and relationships between two-dimensional forms and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 3.2 describes and classifies geometric figures and three-dimensional objects in terms of properties in contexts inclusive of those that can be used to promote awareness of social, cultural and environmental issues, including:3.2.1 sides, angles and diagonals and their relationships, focusing on triangles and quadrilaterals (e.g. types of triangles and quadrilaterals); |
| 3.3 uses vocabulary to describe parallel lines that are cut by a transverse, perpendicular or intersection line, as well as triangles, with reference to angular relationships (e.g. vertically opposite, corresponding);3.4 uses a pair of compasses, a ruler and a protractor for accurately constructing geometric figures so that specific properties may be investigated and nets may be designed;3.5 designs and uses nets to make models of geometric three- dimensional objects that have been studied in the preceding grades and up till now;3.7 uses proportion to describe the effect of expansion and reduction on the properties of geometric figures;3.8 draws and interprets sketches of geometric three-dimensional objects from several perspectives, focusing on the retention of properties. |
| LO 4 |
| MeasuringThe learner is able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulas in a variety of contexts. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 4.1 solves more complicated problems involving time, inclusive of the ratio between time, distance and speed;4.2 solves problems involving the following:4.2.1 length;4.2.2 circumference and area of polygons and circles;4.2.3 volume and exterior area of rectangular prisms and cylinders; |
| 4.3 solves problems using a variety of strategies, including:4.3.1 estimation;4.3.2 calculation to at least two decimal points;4.3.3 use and converting between appropriate S.I. units; |
| 4.5 calculates the following with the use of appropriate formulas:4.5.1 circumference of polygons and circles;4.5.2 area of triangles, right angles and polygons by means of splitting up to triangles and right angles;4.5.3 volume of prisms with triangular and rectangular bases and cylinders; |
| 4.7 estimates, compares, measures and draws triangles accurately to within one degree. |
ACTIVITY 1 – ACTIVITY 5
The memorandum of this learning unit is done by the learners and /or determined by the teacher for corrections.
ACTIVITY 6
1. Both pairs opposite sides are equal.
2. Both pairs opposite sides are parallel.
3. Both pairs opposite angles are equal.
4. Diagonals bisect each other.
5. One pair opposite sides – equal and parallel.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?