| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The ordered pairs can be represented in the form of tabular cells or points of intersection of perpendicular lines. The elements of one set are represented as rows, whereas elements of other set are represented as columns. Look at the representation of ordered pairs by points in the figure for the example given earlier.
Cartesian product

Note that there are a total of 9 intersection points, corresponding to 9 ordered pairs.
Problem 1 : If , find “x” and “y”.
Solution : Two ordered pairs are equal. It means that corresponding elements of the ordered pairs are equal. Hence,
and
Problem 2 : If A = {5,6,7,2}, B={3,5,6,1} and C = {4,1,8}, then find .
Solution : In order to evaluate the given expression, we first find out the intersections given in the brackets.
Thus,
Note that the elements in the given set are not ordered. It is purposely given this way to emphasize that order is requirement of ordered pair – not that of a set.
We have seen that ordered pairs are represented graphically by the points of intersection. The numbers of intersections equal to the product of numbers of rows and columns. Thus, if there are “p” elements in the set “A” and “q” elements in the set “B”, then total numbers of ordered pairs are “pq”. In symbolic notation,
Like other set operations, the product operation can also be applied to a series of sets in sequence. If is a finite family of sets, then their Cartesian product, one after another, is symbolically represented as :
This product is set of group of ordered elements. Each group of ordered elements comprises of “n” elements. This is stated as :
The Cartesian product is set of triplets. This product is defined as :
We can also represent Cartesian product of a given set with itself in terms of Cartesian power. In general,
where “n” is the Cartesian power. If n = 2, then
This Cartesian product is also called Cartesian square.
Problem 3 : If A = {-1,1}, then find Cartesian cube of set A.
Solution : Following the method of writing ordered sequence of numbers, the product can be written as :
The total numbers of elements are 2x2x2 = 8.
The Cartesian product, consisting of ordered triplets of real numbers, represents Cartesian three dimensional space.
Each of the elements in the ordered triplet is a coordinate along an axis and each ordered triplet denotes a point in three dimensional coordinate space.
Cartesian coordinate system
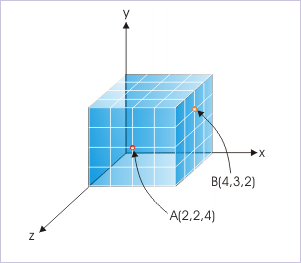
Similarly, the Cartesian product " " consisting of ordered pairs defines a Cartesian plane or Cartesian coordinates of two dimensions. It is for this reason that we call three dimensional rectangular coordinate system as Cartesian coordinate system.
The Cartesian product is set of ordered pair. Now, the order of elements in the ordered pair depends on the position of sets across product sign. If sets "A" and "B" are unequal and non-empty sets, then :
In general, any operation involving Cartesian product that changes the "order" in the "ordered pair" will yield different result.
However, if "A" and "B" are non-empty, but equal sets, then the significance of the order in the "ordered pair" is lost. We can use this fact to formulate a law to verify "equality of sets". Hence, if sets "A" and "B" are two non-empty sets and
Then,
It can also be verified that this condition is true other way also. If sets "A" and "B" are equal sets, then . The two way conditional statements can be symbolically represented with the help of two ways arrow,
The distributive property of product operator holds for other set operators like union, intersection and difference operators. We write equations involving distribution of product operator for each of other operators as :
Here, sets “A”,”B” and “C” are non-empty sets. In order to ascertain distributive property product operator over other set operators we need to check validity of the equations given above.
We can check these relations proceeding from the defining statements. For the time being, we reason that sequence of operation on either side of the equation does not affect the “order” in the “ordered pair”. Hence, distributive property should hold for product operator over three named operators. Let us check this with an example :
1: For distribution over union operator
Similarly,
Hence,
2: For distribution over intersection operator
Similarly,
Hence,
3: For distribution over difference operator
Similarly,
Hence,
Let us consider an arbitrary ordered pair (x,y), which belongs to Cartesian product set “ ”. Then,
By the definition of product of two sets,
By the definition of union of two sets,
By the definition of union of two sets,
But, we had started with " " and used definitions to show that ordered pair “(x,y)” belongs to another set. It means that the other set consists of the elements of the first set – at the least. Thus,
Similarly, we can start with " " and reach the conclusion that :
If sets are subsets of each other, then they are equal. Hence,
Proceeding in the same manner, we can also prove distribution of product operator over intersection and difference operators,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Functions' conversation and receive update notifications?