| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The basis of analyzing isothermal TGA data involves using the Clausius-Clapeyron relation between vapor pressure (p) and temperature (T), [link] , where ∆H sub is the enthalpy of sublimation and R is the gas constant (8.314 J/K.mol).
Since msub data are obtained from TGA data, it is necessary to utilize the Langmuir equation, [link] , that relates the vapor pressure of a solid with its sublimation rate.

After integrating [link] in log form, substituting in [link] , and consolidating the constants, one obtains the useful equality, [link] .
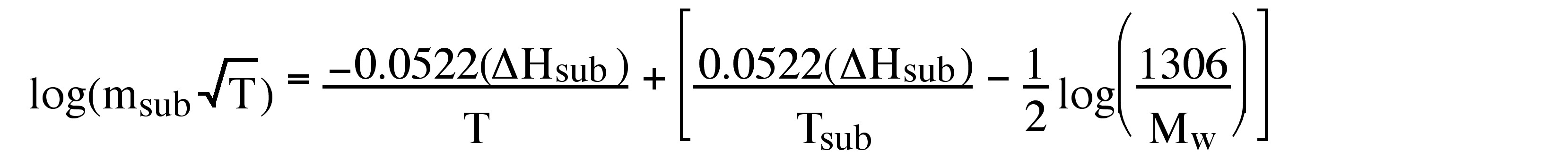
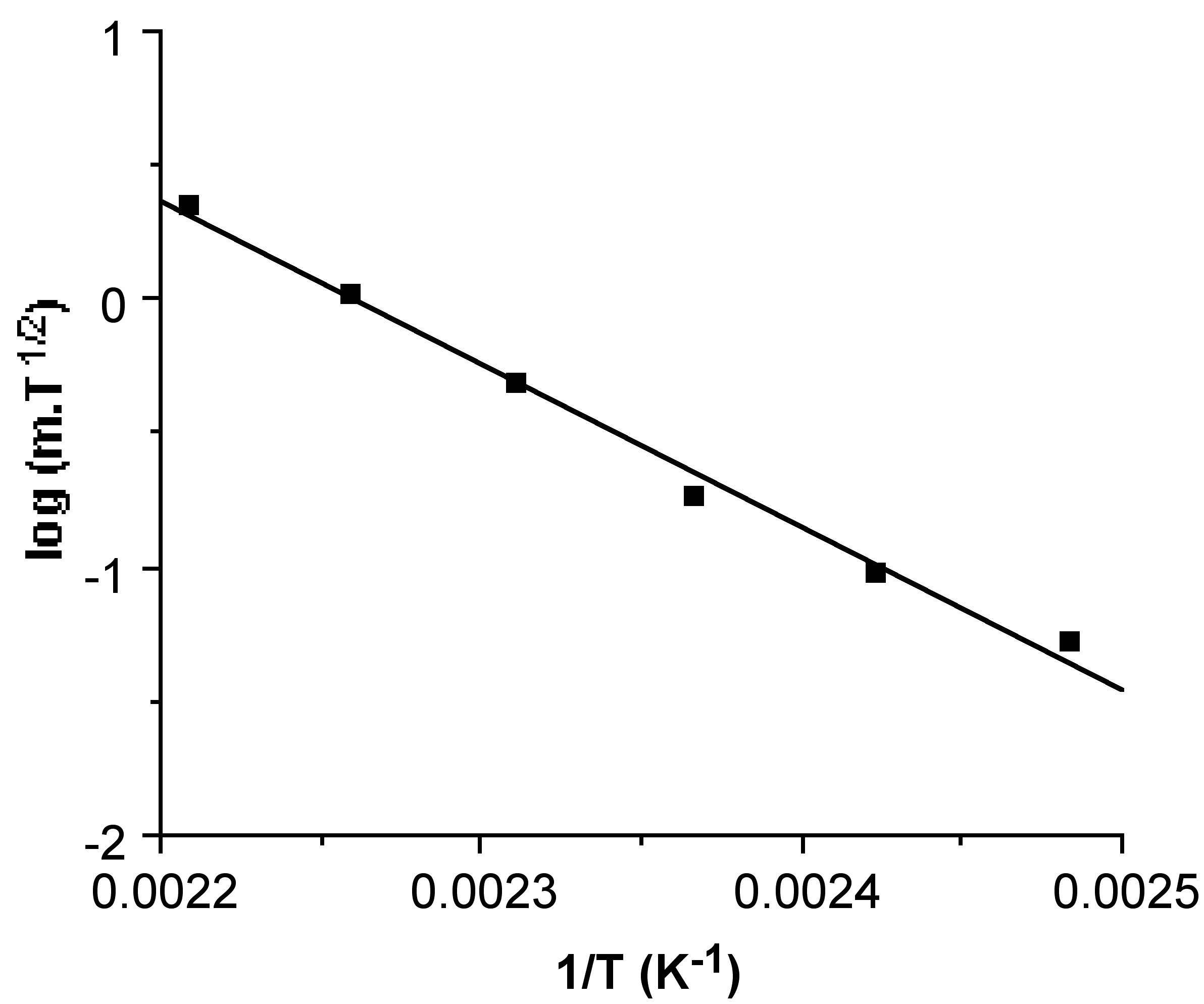
Hence, the linear slope of a log(m sub T 1/2 ) versus 1/T plot yields ΔH sub . An example of a typical plot and the corresponding ΔH sub value is shown in [link] . In addition, the y intercept of such a plot provides a value for T sub , the calculated sublimation temperature at atmospheric pressure.
[link] lists the typical results using the TGA method for a variety of metal β -diketonates, while [link] lists similar values obtained for gallium chalcogenide cubane compounds.
| Compound | ΔH sub (kJ/mol) | ΔS sub (J/K.mol) | T sub calc. (°C) | Calculated vapor pressure @ 150 °C (Torr) |
| Al(acac) 3 | 93 | 220 | 150 | 3.261 |
| Al(tfac) 3 | 74 | 192 | 111 | 9.715 |
| Al(hfac) 3 | 52 | 152 | 70 | 29.120 |
| Cr(acac) 3 | 91 | 216 | 148 | 3.328 |
| Cr(tfac) 3 | 71 | 186 | 109 | 9.910 |
| Cr(hfac) 3 | 46 | 134 | 69 | 29.511 |
| Fe(acac) 3 | 112 | 259 | 161 | 2.781 |
| Fe(tfac) 3 | 96 | 243 | 121 | 8.340 |
| Fe(hfac) 3 | 60 | 169 | 81 | 25.021 |
| Co(acac) 3 | 138 | 311 | 170 | 1.059 |
| Co(tfac) 3 | 119 | 295 | 131 | 3.319 |
| Co(hfac) 3 | 73 | 200 | 90 | 9.132 |
| Compound | ∆H sub (kJ/mol) | ∆S sub (J/K. mol) | T sub calc. (°C) | Calculated vapor pressure @ 150 °C (Torr) |
| [(Me 3 C)GaS] 4 | 110 | 300 | 94 | 22.75 |
| [(EtMe 2 C)GaS] 4 | 124 | 330 | 102 | 18.89 |
| [(Et 2 MeC)GaS] 4 | 137 | 339 | 131 | 1.173 |
| [(Et 3 C)GaS] 4 | 149 | 333 | 175 | 0.018 |
| [(Me 3 C)GaSe)] 4 | 119 | 305 | 116 | 3.668 |
| [(EtMe 2 C)GaSe] 4 | 137 | 344 | 124 | 2.562 |
| [(Et 2 MeC)GaSe] 4 | 147 | 359 | 136 | 0.815 |
| [(Et 3 C)GaSe] 4 | 156 | 339 | 189 | 0.005 |
A common method used to enhance precursor volatility and corresponding efficacy for CVD applications is to incorporate partially ( [link] b) or fully ( [link] c) fluorinated ligands. As may be seen from [link] this substitution does results in significant decrease in the ΔH sub , and thus increased volatility. The observed enhancement in volatility may be rationalized either by an increased amount of intermolecular repulsion due to the additional lone pairs or that the reduced polarizability of fluorine (relative to hydrogen) causes fluorinated ligands to have less intermolecular attractive interactions.
The entropy of sublimation is readily calculated from the ΔH sub and the calculated T sub data, [link] .
[link] and [link] show typical values for metal β-diketonate compounds and gallium chalcogenide cubane compounds, respectively. The range observed for gallium chalcogenide cubane compounds (ΔS sub = 330 ±20 J/K.mol) is slightly larger than values reported for the metal β-diketonates compounds (ΔS sub = 130 - 330 J/K.mol) and organic compounds (100 - 200 J/K.mol), as would be expected for a transformation giving translational and internal degrees of freedom. For any particular chalcogenide, i.e., [(R)GaS] 4 , the lowest ΔS sub are observed for the Me 3 C derivatives, and the largest ΔS sub for the Et 2 MeC derivatives, see [link] . This is in line with the relative increase in the modes of freedom for the alkyl groups in the absence of crystal packing forces.
While the sublimation temperature is an important parameter to determine the suitability of a potential precursor compounds for CVD, it is often preferable to express a compound's volatility in terms of its vapor pressure. However, while it is relatively straightforward to determine the vapor pressure of a liquid or gas, measurements of solids are difficult (e.g., use of the isoteniscopic method) and few laboratories are equipped to perform such experiments. Given that TGA apparatus are increasingly accessible, it would therefore be desirable to have a simple method for vapor pressure determination that can be accomplished on a TGA.
Substitution of [link] into [link] allows for the calculation of the vapor pressure (p) as a function of temperature (T). For example, [link] shows the calculated temperature dependence of the vapor pressure for [(Me 3 C)GaS] 4 . The calculated vapor pressures at 150 °C for metal β-diketonates compounds and gallium chalcogenide cubane compounds are given in [link] and [link] .

The TGA approach to show reasonable agreement with previous measurements. For example, while the value calculated for Fe(acac) 3 (2.78 Torr @ 113 °C) is slightly higher than that measured directly by the isoteniscopic method (0.53 Torr @ 113 °C); however, it should be noted that measurements using the sublimation bulb method obtained values much lower (8 x 10 -3 Torr @ 113 °C). The TGA method offers a suitable alternative to conventional (direct) measurements of vapor pressure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of electronic materials' conversation and receive update notifications?