| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A perfect prime is also called a unison . It is two notes that are the same pitch . A perfect octave is the "same" note an octave - 12 half-steps - higher or lower. A perfect 5th is 7 half-steps. A perfect fourth is 5 half-steps.
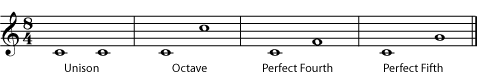
Listen to the octave , perfect fourth , and perfect fifth .
Seconds, thirds, sixths, and sevenths can be major intervals or minor intervals . The minor interval is always a half-step smaller than the major interval.
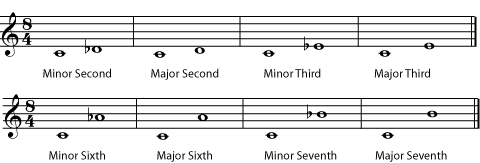
Listen to the minor second , major second , minor third , major third , minor sixth , major sixth , minor seventh , and major seventh .
If an interval is a half-step larger than a perfect or a major interval, it is called augmented . An interval that is a half-step smaller than a perfect or a minor interval is called diminished . A double sharp or double flat is sometimes needed to write an augmented or diminished interval correctly. Always remember, though, that it is the actual distance in half steps between the notes that determines the type of interval, not whether the notes are written as natural, sharp, or double-sharp.
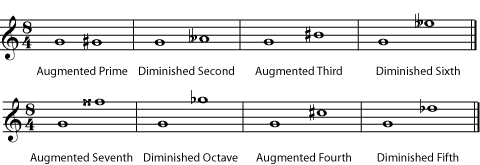
Listen to the augmented prime , diminished second , augmented third , diminished sixth , augmented seventh , diminished octave , augmented fourth , and diminished fifth . Are you surprised that the augmented fourth and diminished fifth sound the same?
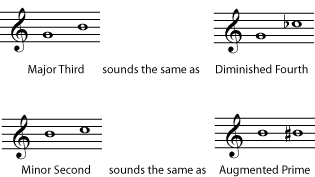
As mentioned above, the diminished fifth and augmented fourth sound the same. Both are six half-steps, or three whole tones , so another term for this interval is a tritone . In Western Music , this unique interval, which cannot be spelled as a major, minor, or perfect interval, is considered unusually dissonant and unstable (tending to want to resolve to another interval).
You have probably noticed by now that the tritone is not the only interval that can be "spelled" in more than one way. In fact, because of enharmonic spellings , the interval for any two pitches can be written in various ways. A major third could be written as a diminished fourth, for example, or a minor second as an augmented prime. Always classify the interval as it is written; the composer had a reason for writing it that way. That reason sometimes has to do with subtle differences in the way different written notes will be interpreted by performers, but it is mostly a matter of placing the notes correctly in the context of the key , the chord , and the evolving harmony . (Please see Beginning Harmonic Analysis for more on that subject.)
To invert any interval, simply imagine that one of the notes has moved one octave, so that the higher note has become the lower and vice-versa. Because inverting an interval only involves moving one note by an octave (it is still essentially the "same" note in the tonal system), intervals that are inversions of each other have a very close relationship in the tonal system.
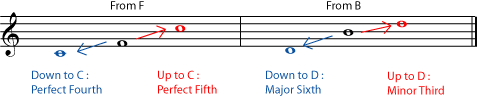
What are the inversions of the following intervals?
Here is a quick summary of the above information, for reference.
| Number of half steps | Common Spelling | Example, from C | Alternate Spelling | Example, from C | Inversion |
| 0 | Perfect Unison (P1) | C | Diminished Second | D double flat | Octave (P8) |
| 1 | Minor Second (m2) | D flat | Augmented Unison | C sharp | Major Seventh (M7) |
| 2 | Major Second (M2) | D | Diminished Third | E double flat | Minor Seventh (m7) |
| 3 | Minor Third (m3) | E flat | Augmented Second | D sharp | Major Sixth (M6) |
| 4 | Major Third (M3) | E | Diminished Fourth | F flat | Minor Sixth (m6) |
| 5 | Perfect Fourth (P4) | F | Augmented Third | E sharp | Perfect Fifth (P5) |
| 6 | Tritone (TT) | F sharp or G flat | Augmented Fourth or Diminished Fifth | F sharp or G flat | Tritone (TT) |
| 7 | Perfect Fifth (P5) | G | Diminished Sixth | A double flat | Perfect Fourth (P4) |
| 8 | Minor Sixth (m6) | A flat | Augmented Fifth | G sharp | Major Third (M3) |
| 9 | Major Sixth (M6) | A | Diminished Seventh | B double flat | Minor Third (m3) |
| 10 | Minor Seventh (m7) | B flat | Augmented Sixth | A sharp | Major Second (M2) |
| 11 | Major Seventh (M7) | B | Diminished Octave | C' flat | Minor Second (m2) |
| 12 | Perfect Octave (P8) | C' | Augmented Seventh | B sharp | Perfect Unison (P1) |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to music theory' conversation and receive update notifications?