| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Motivate why you think you can make a contribution to a specific section:
STEP 4: Homework Individual
To get an idea of what a production implies, it is a good idea to take a close look at the programme of other productions.
Collect examples of programmes of school or professional performances like musicals, revues, etc.
Exhibit these in your classroom or paste them into your journal.
Critically compare two of these programmes and state your preferences:
| P rogramme 1 | P rogramme 2 | |
| Cover/ Front page | ||
| Composition | ||
| Lay-out | ||
| Lay-out of the production team | ||
| Cast |
| Photographs | ||
| Advertisements | ||
| Sponsors | ||
| Others: | ||
STEP 5: Planning with regard to Marketing
Then choose a Production Manager (it may be the educator).
The Production Manager is responsible for the administration.
Divide into the following sections. Each group chooses a leader.
| Fund-raising | Fund-raising co-ordinator |
| Advertising | Publicity co-ordinatorProgramme co-ordinator |
| Tickets | Ticket co-ordinator |
| Refreshments | Refreshments co-ordinator |
Each sub-section hands in a written plan and budget to the Production Manager.
Paste these into your learner journals.
STEP 6: P lanning for the Production itself
All the learners are given the opportunity to participate in the artistic and technical aspects.
Choose a PRODUCER (it may be the educator).
The producer makes the final decision with regard to the production.
Discuss the production.
A production assistant is responsible for the administrative work.
Divide into the following sections. Each group chooses a leader.
| T echnical | Lightning – Lighting Designer and crew |
| Stage – Stage Manager and crew | |
| Sound – Sound Manager and crew | |
| D esign | Decor - Set Designer and crew |
| Costumes – Costume Designer and helpers | |
| Props – Property Manager | |
| Dance – Choreographer and dancers | |
| Music - Music Producer, orchestra and singers |
Each section plans in co-operation with the PRODUCER.
Each section hands in a budget to the PRODUCTION MANAGER.
Planning (in the form of sketches) and budgets are pasted into your learner journals.
Research the "job" you have to do!
SUGGESTIONS:
Limit yourself to one item.
| Learning Outcome(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| creating, interpreting and presentingThe learner will be able to create, interpret and present work in each of the art forms. |
| Assessment Standards(ASe) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| DANCE |
| 1.1 participates in the choreography and presentation of a short dance for a performance or cultural event;1.2 in preparing the body, accurately performs a set warm-up and skill-building sequence, including body conditioning and dance technique in a particular style;1.3 moves across space in movement sequences with co-ordination, musicality, quality, style, balance and control;1.4 learns and performs, with appropriate style and movement quality, works choreographed by others from at least two cultures, which may be: |
| 1.4.1 classical / traditional (African, Eastern or Western); |
| 1.4.2 contemporary; |
| 1.5 creates a dance that fuses steps or styles from more than one South African dance form with a clear beginning, middle and ending. |
| DRAMA |
| 1.6 conducts a simple warm-up routine with the class;1.7 participates in an aspect of planning, organising, advertising, marketing, fund-raising or producing a dramatic item for an audience; |
| MUSIC |
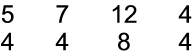 1.9 makes music using voice, available percussion or melodic instruments for performance in meters;1.10 organises and markets a musical performance with regard to planning, advertising, fund-raising and producing; 1.9 makes music using voice, available percussion or melodic instruments for performance in meters;1.10 organises and markets a musical performance with regard to planning, advertising, fund-raising and producing; |
Time Signature
5 4 , 7 4 , 12 8 and 4 4 all refer to specific beats, i.e. how many beats there are in each bar.
Thus far in the modules, the emphasis has been on simple and regular time. Here the learner will come into contact with irregular meters. Follow the explanation of each and let the learners clap the bars repeatedly. Pay attention to the underlying accents.

Examples of irregular meters


Example of a compound time


As soon as the learners are familiar with the respective meters they can perform them as follows:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Arts and culture grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?